

Traceability is the ability to determine the source of anything and everything in manufacturing. Today, it is becoming increasingly important to understand the source when manufacturing parts and products. In some sectors, it is critical to know these sources due to strict regulations, and in other sectors, it plays a key role in improving and maintaining product quality. Due to awareness of safety increases and significant improvements in the quality of the product, traceability has gained importance in delivering insights to a range of industries such as automotive, medical, food, and electronics. Thus, it’s imperative that every manufacturer make traceability a priority!
Traceability helps to trace every manufacturing detail such as processes, raw material procurement, production, consumption, and disposal. It offers various benefits for manufacturers in terms of increasing quality and reducing costs. In this article, we give an in-depth understanding of the increasingly-popular traceability concept in the manufacturing industry, and why it’s vital for the success of your business.
Traceability is formed by Trace and Ability and it enables the manufacturers to collect and document the entire product lifecycle.
Traceability is the ability to track every manufacturing and distribution aspect. It enables tracking every factor right, from raw material procurement and its entry into the factory to the shipment of final products. Through traceability, all the necessary information of the manufacturers, suppliers, and distributors is recorded. This information includes all processes from raw material procurement to machining, assembly, distribution, and sales.
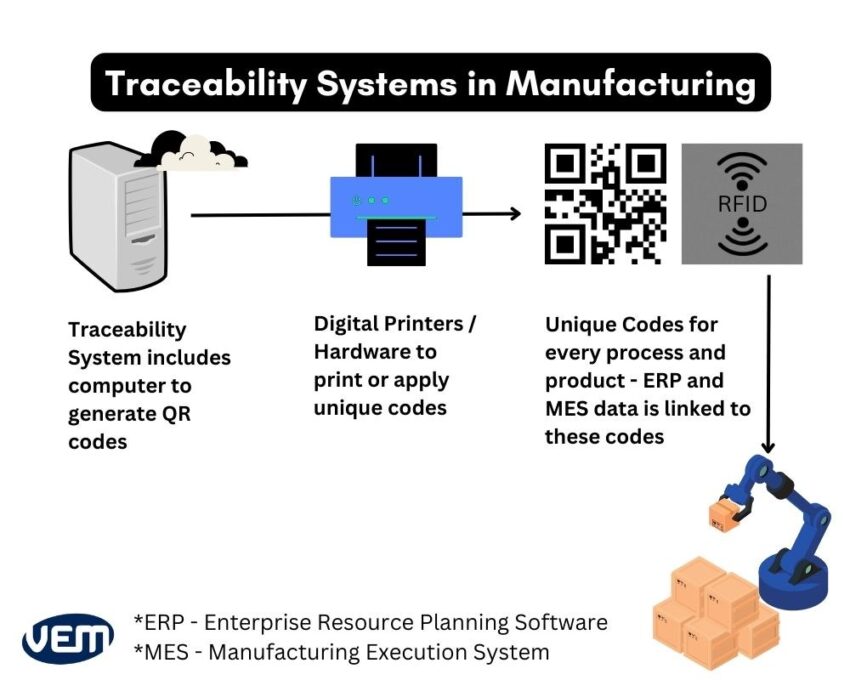
When you implement traceability in your business, you will be able to track every part or component of a part that you produce. You will be able to assess any error throughout the product’s lifecycle. If a problem arises during any stage of the production process, traceability can show where the problem initially emanated. In a nutshell, you can track the source and origin of every raw material, and assess every process and personnel in real-time.
Traceability helps to increase production efficiency and optimize costs, and it also helps to deal with product recalls. It allows a definitive paper trail documenting information on each part which includes inspection results, assembly details, and time spent at each stage.
Now that we understand what traceable manufacturing is, let’s understand what its significance is in manufacturing.
Traceability facilitates root-cause analysis and enables the manufacturers to easily determine and locate when and where a problem occurred. It also describes the details of that problem. Thus, it significantly helps to improve quality and efficiency by giving real-time visibility.
Traceability helps to locate and resolve inefficiencies across the lifecycle of the product and its supply chain. Many times, manufacturing processes can be optimized through traceability to reduce waste, especially by factors that may have been prevented if discovered early enough. Traceability systems enhance visibility and can optimize their production processes to enable efficiency and reduce resource wastage.
For instance: If certain parts that are being produced have defects, it is essential to have that visibility into their whole production process. It may be possible that the defective products are being handled by a specific operator, which means that there are gaps in operator training or it may be possible that the raw material is not dried thoroughly which is causing the defects.
Product recalls can be extremely disruptive to businesses. Traceability is widely implemented by industries to manage avoidable product recalls. It not only lowers the risk of product recalls but also minimizes damages and improves upon challenges that are often faced by manufacturers.
When the origin of components is traceable, there is a higher chance of uncovering the compromised raw materials that might have been compromised before they are used to make your product and distributed. It is much better to stop a mistake from happening than to try to undo one after the product has been shipped.
It is often very difficult to check manufacturing data and to adhere to regulations that are subject to frequent changes; thus, a history management system is essential in today’s time.
The progress of globalization has also increased the requirement of building a history management system that indicates details of the manufacturing process and the plant.
Tracking your production process helps businesses to ensure compliance with respect to regulatory body requirements.
It also ensures quality control by monitoring manufacturing processes. Traceability provides a high-level quality assurance over manufacturing processes by ensuring quality control at every stage.
Traceability helps to manage customer relationships and address customer complaints. If a customer identifies an error in the product, traceability makes it easier to identify where the error may have occurred.
Robust traceability systems also enable organizations to be positioned better in the market. Traceability helps to implement incremental improvements in the product which enables them to develop higher-quality products that can meet customer requirements.
There are various types of businesses that benefit from the implementation of traceability models. These companies observe the highest return on investment due to their supply chain traceability initiatives. Let’s take a look at some of the company types that should consider implementing traceability:
Now that we understand what traceable manufacturing is, let’s understand what its significance is in manufacturing.
Traceability facilitates root-cause analysis and enables the manufacturers to easily determine and locate when and where a problem occurred. It also describes the details of that problem. Thus, it significantly helps to improve quality and efficiency by giving real-time visibility.
In some industries such as pharmaceutical and medical devices, traceability is a requisite and is regulated via the ISO 9001:2015 standards. According to ISO 9001:2015, traceability is required as it helps in product identification and records all the data that may affect its quality. The records enable the creation of a history management system through documented information.
ISO 9001:2015 standard states that the instruments that are used for traceability must be calibrated at specific intervals and they should be protected from damage to ensure that the results are not altered. You can read more about the ISO 9001:2015 standards here.
Real-time visibility of the entire production process can help you improve processes and thereby, its efficiency. Traceability makes it possible to easily spot bottlenecks in production and locate any issues with sub-standard components. Let’s take a look at the various benefits that traceability offers in manufacturing:
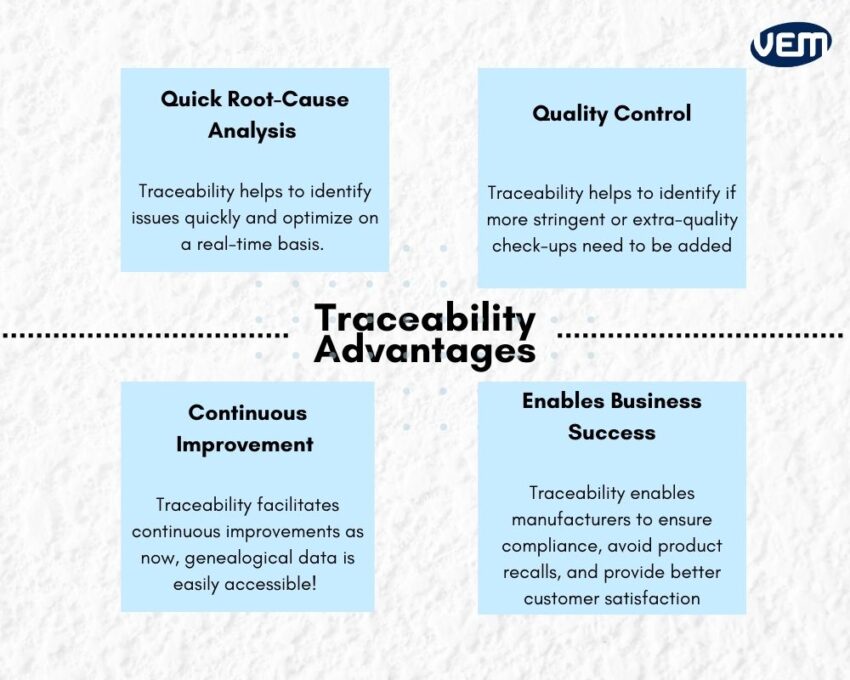
Through traceability, it’s possible to identify issues quickly! It’s also possible to optimize on a real-time basis. The history management system of traceability offers in-depth knowledge and enables manufacturers to quickly locate and find the root cause of problems.
Traceability across the production line helps to identify if more stringent or extra-quality check-ups need to be added. It also helps to understand if anyone is bypassing the quality control systems thereby, increasing accountability on the floor.
Traceability facilitates continuous improvements as now, genealogical data is easily accessible! Since the manufacturers can understand through this data, how parts move through the production line, it helps them to implement improvements continuously, throughout the production cycle.
Traceability has a multi-fold advantage. It enables manufacturers to ensure compliance and quality control, avoid product recalls, and provide better customer satisfaction. Thus, it holistically promotes business success.
Traceability requires adopting an identification or coding system. These systems enable unique tagging of everything that forms the manufacturing process. These systems include individual products, lots, or production in a particular geographical area.
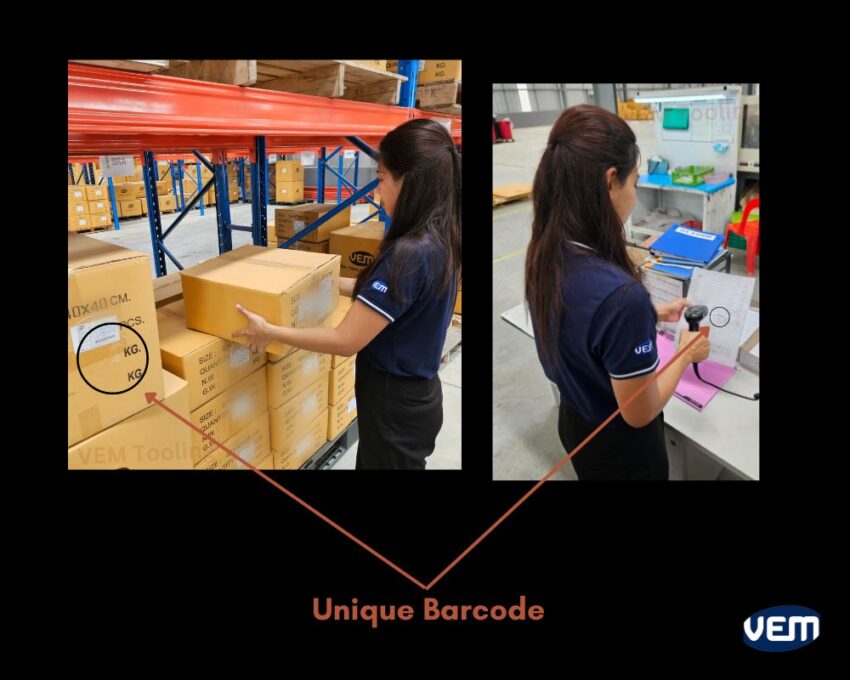

Traceability involves technologies that can mark parts as they enter the assembly on a permanent basis. There are various technologies that an organization can adopt and it may utilize either 2D bar codes, data matrix ID, or RFID tags. Once the manufacturing process for any product or part begins, the ID will be captured in real-time. This ID will be transmitted to a central database, along with the work information of each workstation. This helps to create a history management system as the part/product undergoes its lifecycle. You should note that there are 2 primary components that create an effective and robust traceability system. These are listed below:
When complete manufacturing history is accumulated to be available, it is said to be completely traceable. Typically, components are tagged on arrival at the manufacturing unit or the factory.
Modern technologies have enabled automated tracking of production cycles. There are various technologies and technical processes that are implemented for tracking and traceability. Such technologies help manufacturers to monitor parts and products along the production line, and record all relevant data. In addition, all the reports and information can be tracked through a product genealogy or a traceability app.
Technologies such as barcodes and scanners help to track parts and products easily at every station. It also helps to remind workers on the shop floor by simply adding a step to digital work instructions instead of manually notifying them.
You should note that smart manufacturing companies track and trace every aspect of the manufacturing cycle. This enables them to avoid any type of non-compliance and avoidable errors. We have listed some of these technologies below:

If you are planning to implement traceability, you will need to choose unique identifiers. To choose between unique identifiers such as QR codes, data matrix, or RFID, you must consider various factors such as the product nature, the use case, and security. Let’s take a look at the various considerations that you should pay attention to in order to choose unique identifiers for your product:
You should note that there are different implications in terms of cost and process changes if you are printing codes on packaging or product, or applying codes on a label. The nature of your product and packaging greatly influences the type of unique identifier you should choose for your product. These factors include shapes, curvature, materials, and substrates.
You should note that data matrix and QR codes are more resistant to wear and tear and deformity. In addition, QR codes are easily scannable on curved surfaces. Thus, such factors play an important role in choosing unique identifiers for your project.
The next consideration should be what is the use case that the unique identifier is being used for.
For instance: QR codes and RFID can be easily scanned by not only the manufacturers in the supply chain but also the customer. It thus provides traceability data from the manufacturing unit to the customer in the market. In another case, data matrix codes are popularly implemented for internal and compliance traceability but they cannot be easily scanned by the customers. Thus, they are not able to provide complete route-to-market and end-customer information.
It is important to consider a suitable position to scan the product from the customer’s point of view.
You should note that front labels are the most common but codes and tags can also be placed under the lid or tag if they are intended to be scanned only after the product is opened. In addition, codes like barcodes may be too big for certain applications.
There are various unique identifier solutions with security features. These can be implemented if your project requires using security features.
For instance: Secure QR codes are used in many traceability projects as an anti-counterfeiting component.
Another factor that should be considered while choosing a unique identifier for your product is the cost factor. QR codes are generally the least expensive whereas RFID and NFC are more expensive and are thus used more on higher-value items. RFID and NFC are costlier because they have hardware costs associated with them and they need to be applied with a special process.
Although many industries benefit from traceability, it is more of a pressing requirement in certain industries. Traceability along with product serialization is also a regulatory requirement to prove compliance. Let’s take a look at some examples:
There are various organizations that maintain standards for unique identifiers such as GS1. Their standards cover barcodes, QR codes, data matrix, and more.
The traceability of the supply chain can be segmented mainly into 2 types i.e. Forward and Backward Traceability. Furthermore, there are 2 more types of traceability in manufacturing and they are referred to as product tracking and tracing. Let’s understand these types further in detail:
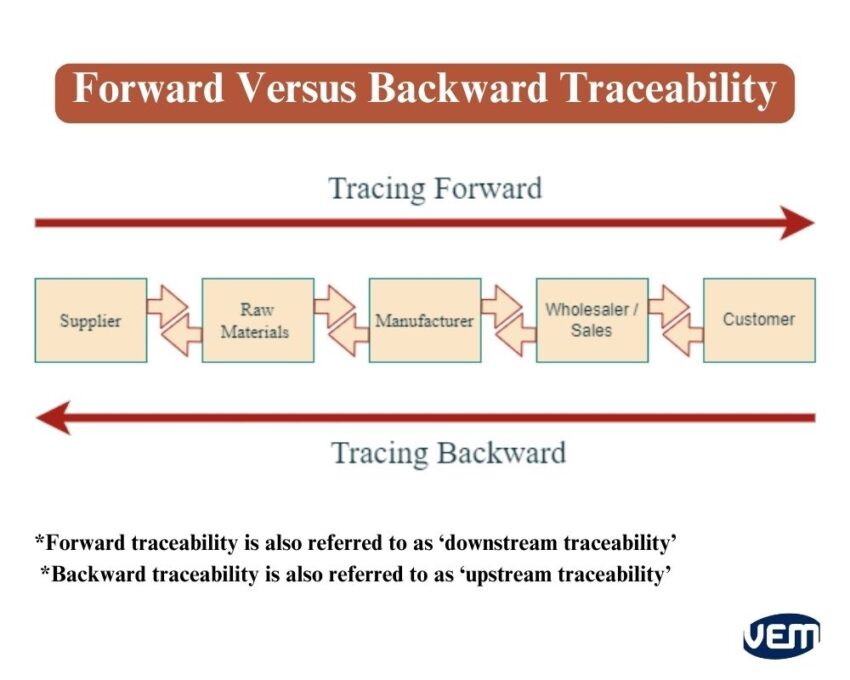
Forward traceability is also referred to as ‘downstream traceability’. This type of traceability traces the product after production to the customer. It helps to trace all the way from the raw materials to the finished product and then finally, the consumer.
Forward traceability is extremely effective in the case of defective products and product recalls. If a defect is detected in a particular part, it is easily identifiable via forward traceability and quick action can be taken to identify and recall the product containing the defective part. It is thus useful for delivering better customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Backward traceability is also referred to as ‘upstream traceability’. This type of traceability follows the journey of a finished product backward and can be traced all the way back to the original source i.e., raw materials. Backward traceability also refers to the tracing of products against the logistical chain, i.e., from the consumer to the original producer.
For instance: In the case of medical devices, backward traceability can identify where the product originally came from before reaching the consumer. It can also identify all the factories and all the processes that the medical device went through before reaching the end customer.
Product tracking enables one to follow a specific product’s path throughout the production cycle. The purpose here is to avoid any type of logistical errors that may arise during production. These products are thus continuously monitored for logistical purposes.
Product tracing helps manufacturers to identify the origin of a product batch. This is achieved by referencing records within the supply chain. Product tracing helps to determine if a particular batch is faulty and thus, you can dispose of only that particular batch. Product tracing thus, helps companies to save on resources and avoid product recalls.
Traceability can be viewed through two perspectives: chain and internal traceability. Let’s understand these perspectives further, in detail:
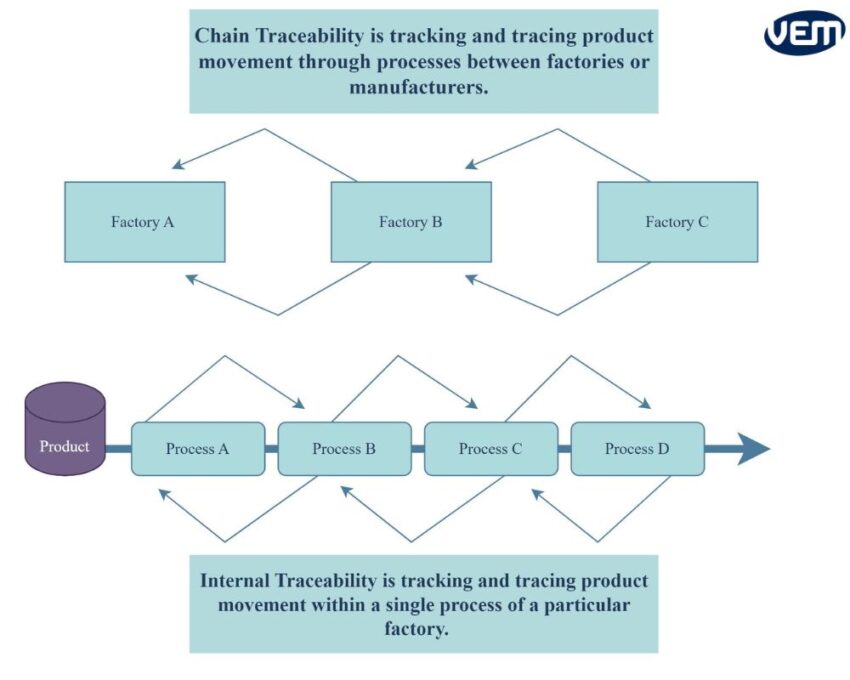
Chain traceability refers to the history of raw material procurement to machining, distribution, and sales that can be traced forward or backward. Chain traceability allows manufacturers to monitor the delivery of their products through forward traceability and it also enables companies and consumers to trace the product back to its origin through backward traceability.
Chain traceability allows manufacturers ease of investigation and avoids product recall. It also helps consumers to select highly reliable products!
Internal traceability is most commonly associated with large businesses and it refers to monitoring a specific part of the supply chain. It is often a limited specific area, such as a single company or plant. Internal traceability is especially helpful to trace components and materials within a single company. In companies that have multiple sites, often in different geographical locations, it can be difficult to pinpoint process inconsistencies or errors. Internal traceability helps to pinpoint any problems that may occur within a particular stage of the manufacturing process.
Management and utilization of the manufacturing history and inspection results of these parts by the plant can also be regarded as internal traceability.
Implementing traceability in manufacturing is adopting digital advancements to incorporate fast-tracked, flexible solutions.
Today, various manufacturing units have managed to incorporate quick solutions through well-integrated traceability systems. They have managed to streamline their operations in order to manufacture high-quality plastic parts with minimal product recalls.
Our partner PlanTool provides advanced ERP systems and machine connectivity, tailormade for the tooling and injection molding industry.