

Supply chains follow a linear progression and here, the output of one step is the input of the next step. Thus, it is critical that every stage is designed with utmost detail and if there is any error at any of the supply chain stages, then the entire supply chain is disrupted!
Today, supply chain networks are not only sophisticated but they are also more flexible and efficient! You should note, however, that while they have extensively evolved, they have also become more complex.
Supply chains incorporate and cover all aspects of production, product development, and information systems that are needed to manage production. Its effective management is every stakeholder’s effort and here, the aim is to develop and implement processes that make the entire cycle as efficient and economical as possible. Let’s further understand supply chain management and how you can implement it for your business.
Supply chain management, abbreviated as SCM, is primarily ensuring that all processes within the supply chain are optimized to improve efficiencies and cut costs. SCM involves streamlining operations to manufacture high-quality products that maximize customer experience thereby, gaining a competitive edge in the marketplace.
SCM connects production, shipment, and distribution, centrally. It helps to manage the supply chain more effectively and this is achieved by keeping tight control and vigilance upon production, distribution, sales, and inventories. Let’s understand further the process of supply chain management:
The sole aim of supply chain management is to maximize efficiency while optimizing costs. An efficient supply chain management ensures that the losses are minimized and there are no lawsuits that can occur due to faulty product releases or malpractices. This is achieved by managing all aspects of the supply chain, its logistics, and its inventory.
To ensure that your products are traceable, you need to implement a robust system that follows the product manufacturing journey all the way, from raw materials to processing and distribution. This enables gathering information on various components that are vital for product identification.
The key to precise and accurate information via product and part traceability is having a centralized system. There are various platforms and technologies that help to create a centralized traceability solution which is why it is more achievable than ever!
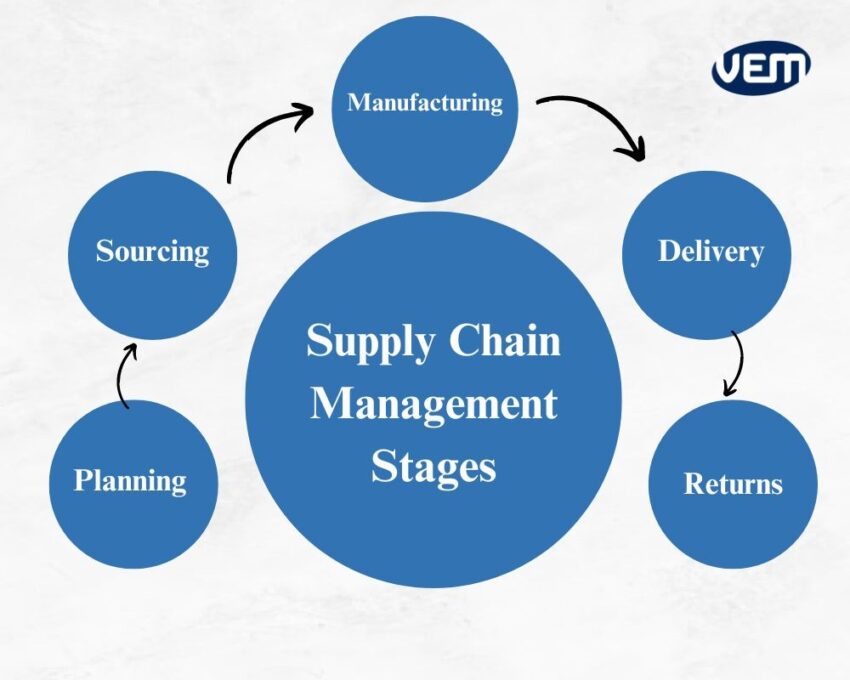
The management of the supply chain has 5 major stages and they are categorized below:
The planning phase consists of developing a strategy for the supply chain, while the rest of the phases consist of outlining key requirements for executing the developed strategy. In order to avoid bottlenecks and have an efficient supply chain, it is imperative for any company or manufacturing unit to develop expertise in all stages. Let’s understand these stages more in-dept:
The planning stage is the precursor of supply chain management. The SCM process for the planning stage is to develop a strategy to meet customer requirements and consequentially, its manufacturing demands. It is crucial for the manufacturing units to predict with approximate accuracy the requirements. These details include raw material requirements that may be needed at various manufacturing stations, equipment capacity, and staffing requirements. In addition, it is necessary to outline the limitations and any bottlenecks that can occur during production.
Many organizations make use of ERP systems to aggregate information and develop the planning stage. ERP Systems include supply chain analytics and materials management features which help to develop strategic plans in order to meet customer and project requirements.
The sourcing stage of SCM entails shortlisting vendors and working with them to supply raw materials that are needed for the project and throughout the manufacturing process. This stage ensures the following requirements of the SCM:
At this stage, a manufacturing unit transforms raw materials into products. The final product that is manufactured in this stage is entirely the ultimate goal of the project but the manufacturing process is still not the final stage of supply chain management.
This stage is further divided into various sub-tasks such as operations, testing, assembly, and packaging. In this stage, the products are manufactured and they move through various stations of scheduling, production, quality testing, packing, and storage. This stage also gives opportunities to streamline any aspect that may be deficient otherwise such as apt quality testing and employee training.
The sales and delivery are the next stages after manufacturing! It is imperative to have a robust distribution and delivery process as this is the first time the customer will interact with the product and hence, this stage can also be viewed as a major contributor to the image of the brand.
A good SCM process incorporates robust logistic capabilities and delivery channels. This helps to ensure timely, safe, and cost-effective delivery of the products. It also incorporates the inclusion of a diversified distribution method or a backup plan in case a particular method of transportation is temporarily unavailable. For instance: A company’s delivery process can be impacted or interrupted by unprecedented rainfall or snowfall. You should also note that at this stage, inventory and warehouse management systems also need to be incorporated as it makes the distribution and delivery process seamless.
Returns are the final stage of the supply chain management process. It’s often referred to as reverse logistics and includes various types of product returns such as defective products, products that did not meet customer expectations, or discontinued products. This stage also includes elements from other stages such as inventory, transportation management, and customer support for easy returns
In this process, the company must ensure to include processes that carry out not only easy returns but correctly refund the customer for the returned product.
Establishing an effective customer return platform isn’t just a process but it can also serve as informative articles to businesses for identifying defective and non-conforming products. If the underlying cause of a customer return is not noted, then future returns are likely to persist.
Supply chain management helps to achieve various business objectives such as reducing product recalls, improving product quality, keeping lawsuits at bay, improving customer relationships, and building a strong brand image. Overall, supply chain management creates various opportunities to improve profits and gives a competitive advantage in the market. Let’s take a look at some of the supply chain management benefits:

Every system has some building blocks that are crucial to its functioning and it’s the same for supply chain management!
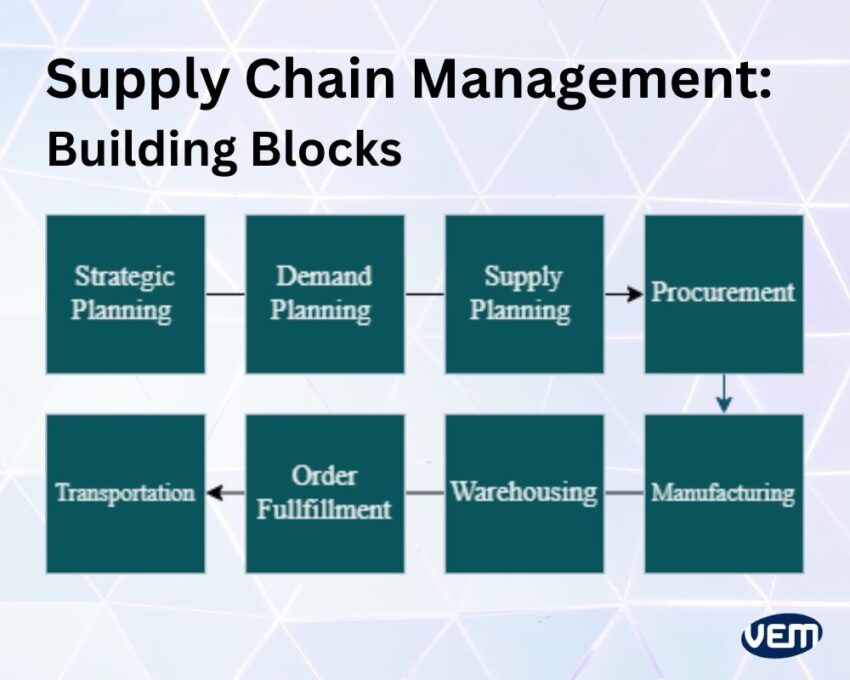
The building blocks of supply chain management are listed below:
All of the above-mentioned processes are crucial and they thread the supply chain management to be efficient. Let’s understand these further in detail:
This is the first building block of the supply chain management process. Strategic planning can be further subdivided into supply chain design and sourcing.
Let’s take a look at the next building block of the supply chain management process i.e. the demand planning process. This is further subdivided into various types which are listed below:
This process primarily involves planning at various stages of the supply chain. Let’s get a more in-depth understanding of these stages:
The manufacturing process is the heart of production and it involves a detailed scheduling process and a manufacturing execution process. Let’s understand these processes further:
This stage is the management of the warehouse at various stages. Let’s understand these further in detail:
The transportation process also includes a planning and execution stage. Together, this entire process provides not only a complete but an integrated solution that can create, execute, and monitor shipments.
Since the terminologies and concepts are interdependent, they are often used interchangeably. In this section, we explain the basic similarities and differences between supply chains and supply chain management.

A supply chain is a complex network that consists of companies, resources, activities, employees, and technologies. These are necessary and are employed to manufacture a product and thereby, sell it. A supply chain includes end-to-end manufacturing of products. The functions of a supply chain are not only limited to product development and production but also include marketing, distribution, and customer service. It starts with raw material delivery from a vendor to the manufacturer and ends with the delivery of the finished product to the final customer or consumer.
Supply chain management, on the other hand, oversees each and every aspect of the supply chain cycle, right from the creation stage to its final sale. The aim to implement SCM is to understand if efficiencies can be improved and costs can be cut-down. Thus, a robust SCM can increase revenues and greatly impact a company’s bottom line. The SCM has 5 main stages that start from designing the supply chain to handling returns in an efficient manner. It also oversees the sourcing of raw materials, manufacturing, and delivery.
If a supply chain consists of a complex network of suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and the customer then the management of the supply chain is the orchestration between these networks that comprises raw material procurement, management, manufacturing, delivery, and providing exceptional customer service. Now that we have understood what is the difference between supply chain and supply chain management, let’s understand the stages of supply chain management.
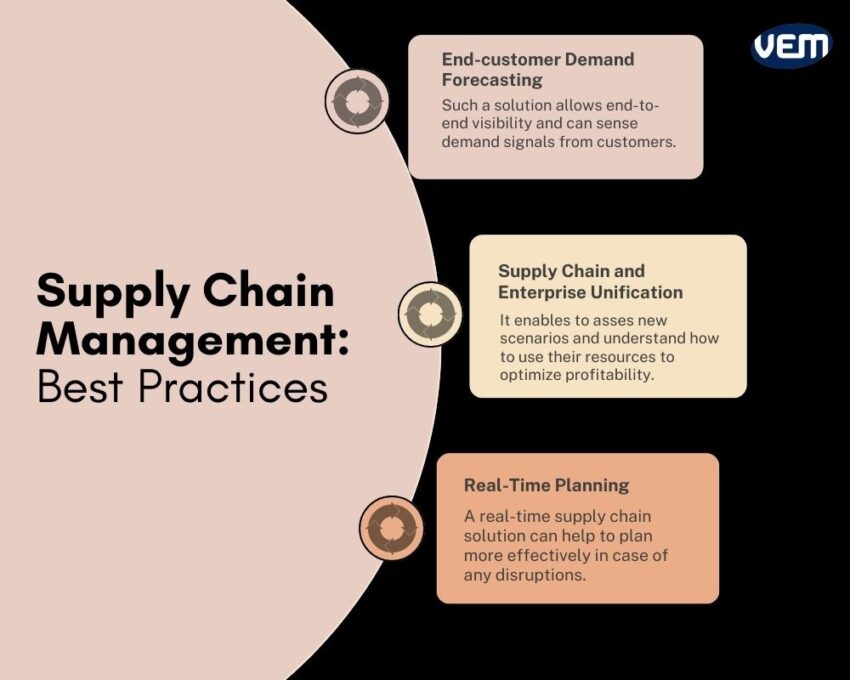
Usually, companies rely on historical data to forecast the possibility of disruptions in the supply chain. This can, however; be avoided by incorporating a real-time supply chain solution. Such solutions help to plan more effectively in case of any disruptions. Incorporating a solution that uses real-time data enables planning with greater accuracy.
It is an ongoing challenge to anticipate customers’ demands in a timely manner. Thus, a solution that allows end-to-end visibility across the supply chain is crucial. Such a solution can sense demand signals from customers.
Collaborating real-time supply chain and enterprise-wide solutions can enable stakeholders to asses new scenarios and understand how to use their resources to optimize profitability when an unforeseen event happens.
Supply chain management enables manufacturers to reduce overhead costs and improve efficiency. You can explore Supply Chain Management through the current systems in VEM-Tooling!
We aim to optimize processes and provide unmatched transparency during the whole manufacturing process.
To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.