

Consistent quality is of paramount importance in the manufacturing industry. This is especially critical in the case of complex geometries. Manufacturing high-quality parts consistently requires manufacturers to follow precise design and engineering processes. In addition, they need to strictly comply with the industry standards. A valuable tool that helps manufacturers achieve the same is PPAP, abbreviated for the Production Part Approval Process.
Today, the manufacturing industry is extremely competitive. PPAP enables manufacturers to meet rigorous standards consistently and thus, establishes confidence in customers for suppliers and their processes. Initially, PPAP was largely employed by the automotive and aerospace industries but today, it’s employed by several industries to manufacture high-quality parts consistently. In this article, we discuss PPAP and its significance in detail.
PPAP is a standardized framework that ensures the processes and tools used to manufacture parts are optimized to deliver as per the customer requirements consistently.
The PPAP process builds confidence in customers for suppliers through clearly defined specifications and guidelines. In addition, PPAP enables manufacturers to demonstrate how risk is identified and mitigated through extensive documentation as proof. It ensures that the manufacturer is capable of meeting customer’s requirements.
You should note that the PPAP is similar to developing a strategy. All PPAP submissions are not the same and thus, a negotiation must take place.
A PPAP negotiation directly occurs between the customer and supplier. This negotiation ensures that both the supplier and the customer have the same expectations. It is carried out to confirm the expectations of PPAP elements.
Typically, the supplier guides the customer through an established report such as FMEA (Failure Modes and Effects Analysis), or MSA (Measurement Statistical Analysis) to help them understand the process.
PPAP is a critical component and an output of APQP. Let’s understand the role of PPAP in APQP:
APQP, abbreviated for advanced product quality planning, is an efficient process for launching a new product in the market or incorporating changes after the product is released.
APQP ensures that the product meets the expected customer requirements and is performed through a CFT (cross-functional team) composed of professionals from the design, engineering, manufacturing, quality, and distribution areas.
PPAP is an essential segment of APQP and PPAP ensures quality and consistency in production. If the PPAP results don’t meet the expectations of the customer, it’s typically indicative that the APQP process isn’t working correctly.
PPAP plays a crucial role in confirming consistent production in the APQP system. If the results are not as per the expectation, then an investigation is carried out to understand the deficiencies.
The PPAP process demonstrates documentary evidence to ensure that the manufacturing processes can deliver parts that meet the customer’s requirements consistently. To ensure the same, the supplier must submit a PPAP package. On the other hand, APQP’s purpose is to proactively identify and resolve potential quality problems.
PPAP levels of submission are typically classified into 5 levels. These 5 PPAP levels of submission are categorized according to the complexity and criticality of the part. Each of the 5 PPAP levels of submission has varying requirements and these are listed in the below infographic:
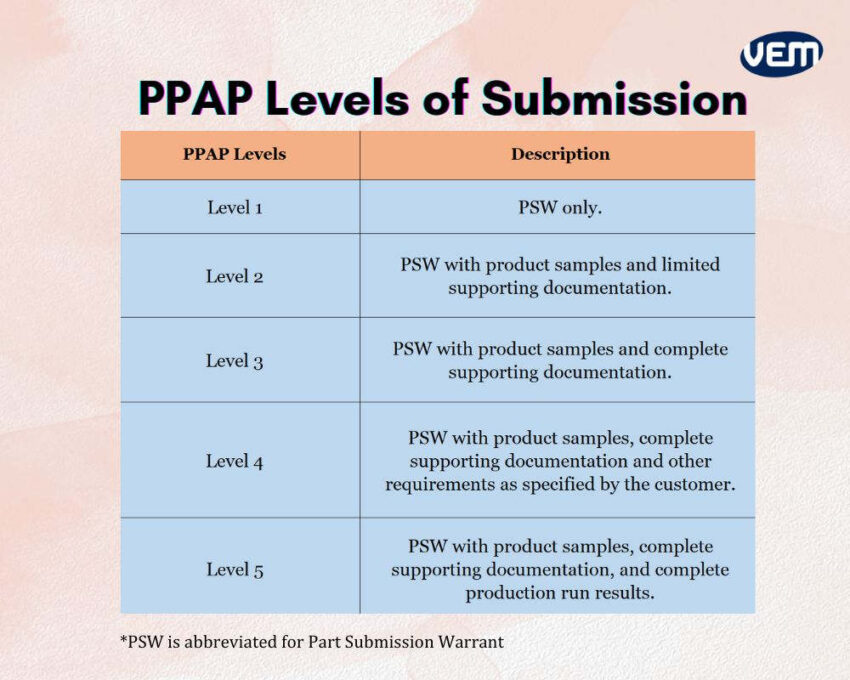
Each PPAP level requires a PSW, abbreviated for Part Submission Warrant. The PSW document summarizes the PPAP contents which must be approved by both the supplier and the customer.
Depending upon the levels, PPAP elements are included or excluded in a PPAP submission. You should note that among all the PPAP levels, level 3 PPAP is the most common of all the levels as it requires PSW submission with product samples and complete supporting data.
Selecting the correct PPAP level is a crucial decision as it ensures that the PPAP submission meets the expectations of the customer, maintains quality, and helps to manage risk. Let’s understand these factors further:
The first factor that influences PPAP levels of submission is the company’s internal standards or industry regulations.
If the part geometry is complex or includes critical functions, then more comprehensive documentation will be required. It is imperative to ensure that every aspect of the design and manufacturing process is validated and thus, the PPAP submission may require the manufacturer to include Design and Process FMEA along with other documentation. Accordingly, a higher level of PPAP submission i.e. levels 3, 4, or 5 may be required.
If the overall function of the part is critical, then thorough documentation will be required. There may be extensive testing and an engineering team’s approval required to ensure that all specifications are met. Thus, higher levels of PPAP submission i.e. levels 3, 4, or 5 will be required if the criticality of the part function is higher.
PPAP is an essential step in the manufacturing process, ensuring that the products meet customer expectations. It encourages a consistent part approval process and improves product quality. In addition, it increases customer satisfaction and provides evidence of process stability.

The very first purpose of PPAP is quality assurance! It ensures that the manufacturing process consistently produces parts that meet all the specifications and are free from defects. PPAP establishes a standardized process for documentation, validation, and approval to ensure that the product meets the expected requirements.
PPAP instills confidence in customers, as it ensures that their expectations will be met and the parts will be manufactured as per the requirements of the customer. It ensures that the manufacturers produce quality parts according to the customer specifications consistently.
To meet customer specifications consistently, a PPAP needs to be implemented into the QMS i.e. Quality Management System. In addition, PPAP also creates a consistent approval process between the customer and manufacturer. It also ensures compliance with industry standards
PPAP is especially helpful in risk mitigation. It enables manufacturers to identify various risks and minimize the occurrence of defects and deviations from the required quality standards.
PPAP helps manufacturers with regulatory compliance. This is crucial where adherence to standards is critical. For instance: automotive components and medical devices.
PPAP thoroughly vets the production process thus, enabling manufacturers to proactively identify, analyze, and resolve potential issues.
PPAP establishes an effective communication channel between suppliers and customers. It helps manufacturers to create detailed documentation and submission of product samples. Thus, the PPAP process aligns the manufacturing process with the product specifications.
Process standardization reduces variability and streamlines processes.
Due to PPAP, a standardized framework is established. This framework validates production processes and ensures that each and everyone follows a uniform approach in manufacturing the product.
PPAP encourages continuous improvement through feedback received during the PPAP approval process. You should note that PPAP provides valuable insights and manufacturers can use this information to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. They can also take proactive measures to implement corrective actions.
PPAP submissions can be extremely complex. Let’s understand some challenging aspects of PPAP submissions:
An extremely challenging aspect of PPAP submission is its extensive documentation. The various elements of PPAP submission need to be managed and accurately completed which requires meticulous attention to detail. You should note missing or incomplete documents can delay approval.
The next challenging aspect is the lack of standardization. If there is variability in documentation and processes, it can lead to inconsistencies. Thus, it’s crucial to standardize PPAP documentation and to maintain process consistency.
The communication gap is another challenging aspect of PPAP submission. If the communication between teams is poor, it can lead to delays and errors.
A PPAP process involves three stages. Let’s understand these stages further:
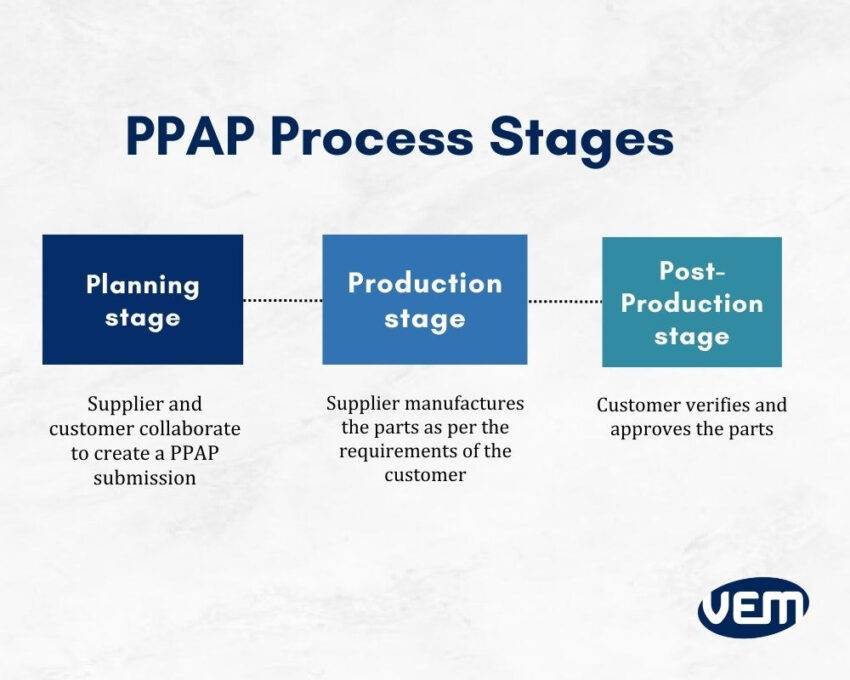
A PPAP process is required when there is a new part submission or anytime a new change to an existing part or process is planned. It is also required for approval to change. You should note that a customer can request a PPAP at any time during the product’s lifecycle.
A PPAP process is conducted via systematic steps. Let’s understand how is PPAP process performed:
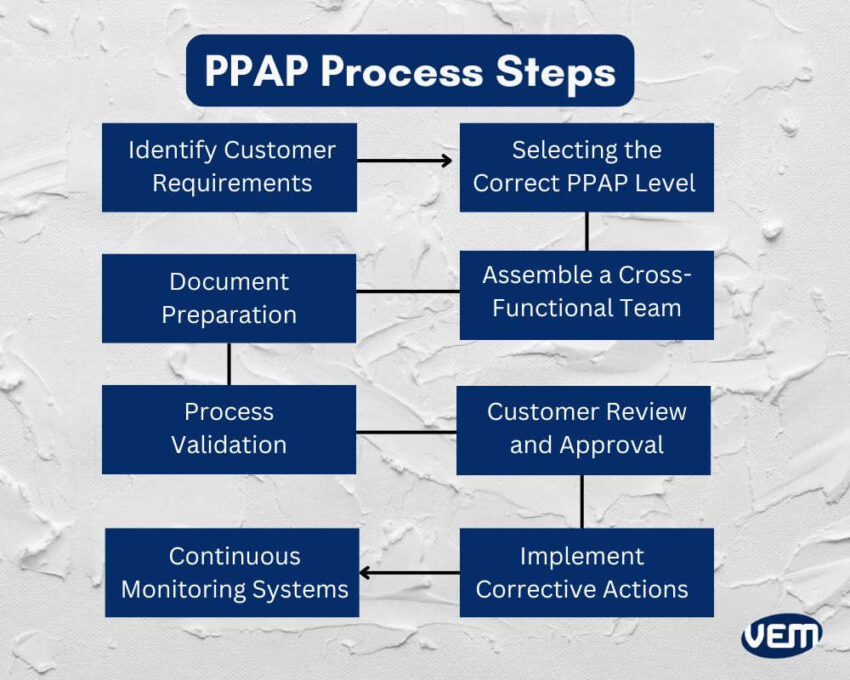
The first step is to identify the customer requirements. You must review the specific requirements and note the expectations for the parts.
The next step is to determine the PPAP submission level. It’s based upon the industry and customer requirements, along with part criticality.
A cross-functional team helps to comprehensively include various aspects of the PPAP process such as design, manufacturing, quality, etc.
In this step, the required documentation for PPAP submission is collected and included in the package. It requires assembling the various PPAP elements.
The next step is ensuring the process meets the quality standards consistently. The manufacturing process should be validated by conducting initial production runs to verify that all the tools and equipment are in optimal condition.
The PPAP package is submitted to the customer for review and approval. The customer either approves the PPAP package or requests corrective actions. In this step, clear communication is critical between the supplier and the customer.
If corrective actions are requested by the customer, then the necessary changes are implemented. The revised package is submitted to the customer for re-approval.
If there are any changes in the process, it needs to be reflected in the PPAP documentation. Thus, a system for continuous monitoring of the production process must be incorporated.
PPAP submissions are extremely complex and detail-oriented. It enlists all the information that’s required to approve a production part and includes various details such as the manufacturing process, specifications, and test results.
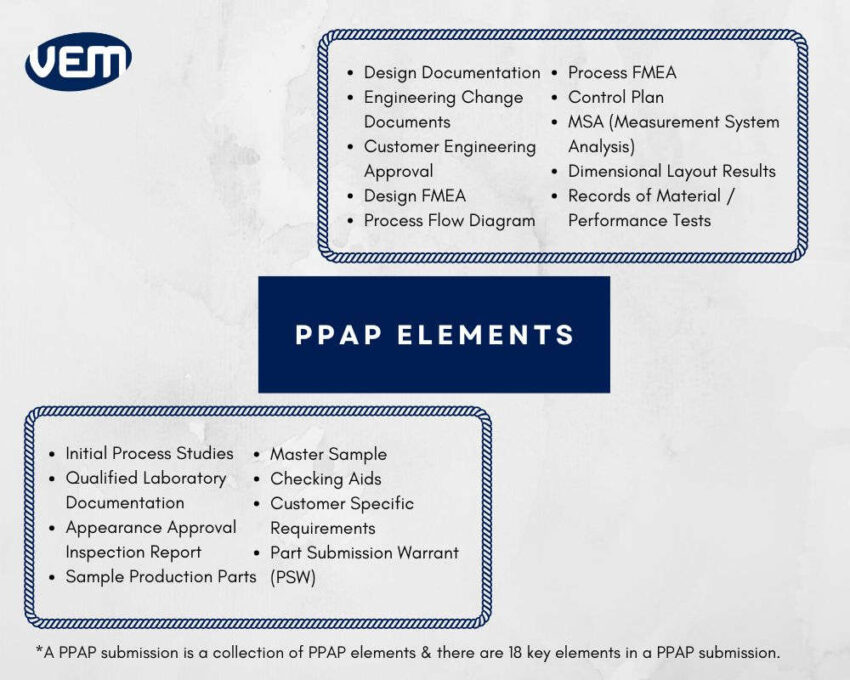
A PPAP submission is a collection of PPAP elements that are verified to produce a quality product as per the customer’s requirements. In a PPAP submission, all the elements are not required but every PPAP submission package contains a Part Submission Warrant that is a summary of the overall PPAP and as a general approval document.
There are 18 key elements in a PPAP submission.
Let’s understand the PPAP elements further:
Design documentation is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing and production process. The goal of design documentation is to ensure that the product meets the market requirements.
In design documentation, each part of the product must be ballooned so that the inspection results can be corresponded with. It includes print notes, standard tolerance notes, and other specifications that are relevant to the part design. A design documentation ensures that the supplier and customer are both discussing the same part.
An ECD is only required if there is a change. If the PPAP is required due to a change, then the documentation that requests and approves the change must be included in the PPAP package.
An Engineering change documentation records all engineering changes that are performed. It also includes the supporting documentation and history of the change.
Many times, a “temporary deviation” is required to send parts to the customer before the PPAP is complete for onsite testing. If required, the supplier must provide evidence of approval by the customer engineering department. When the testing is complete, the engineers will give an approval form for it to be included in the PPAP submission.
DFMEA, abbreviated for Design Failure Mode and Effect Analysis is a specific process for the design stage and it helps to identify all the possible failure modes and their effects during the design process.
DFMEA is a cross-functional activity and it allows the design team to predict the potential failures of the product.
A process flow diagram is a graphical representation of a process that outlines the entire process of manufacturing the part and assembling the component. It should include all the main steps of part processing including incoming material, measuring, assembly, inspection, and shipping. A process flow diagram facilitates communication and understanding of the process.
PFMEA, abbreviated for process failure mode and effects analysis, is a specific process to review all the steps in the production process. It identifies and analyzes potential hazards during the production.
The control plan is PMEA’s output. It provides further detailed information on how the potential issues are checked for during the inspection or the assembly process. It enlists all product special characteristics and inspection methods that are required to deliver products that meet the quality requirements of the customer consistently.
MSA, abbreviated for measurement system analysis, is used to measure the variability of a process. It typically includes Gage Repeatability & Reproducibility (GR&R) for measurement of equipment that is applied during quality control checks or assembly.
The calibration records for all gauges and measurement equipment must be included in the MSA. This analysis provides you with the mean and standard deviation to help you understand your process.
A dimensional layout result list includes product specifications, characteristics, and measurement results. It also provides an assessment report indicating whether the dimension has passed or failed. Generally, a minimum of 6 pieces are reported per product.
The records of material or performance tests include a summary of every test performed on the part. It enlists all the individual tests, their performance date, results, and pass or fail inspection results.
This summary is usually listed in the DVP&R form (Design Verification Plan and Report). The DVP&R is reviewed and signed off by both the customer and supplier to indicate that all the required tests have been conducted.
Initial process studies are conducted on all production processes. It includes SPC i.e. statistical process control charts for critical characteristics. Initial process studies of PPAP elements indicate that the critical processes are stable, and are close to the intended nominal value.
This particular PPAP element consists of industry certifications for any laboratory that was involved in completing the validation testing. It could be an in-house test lab or any other contractual testing lab.
AAI, abbreviated for Appearance Approval Inspection report verifies that the final product meets all the required parameters for the appearance of the design. It indicates that the customer has inspected the design specifications of the finished product or the part. AAI report includes information regarding color, textures, fits, etc.
In this PPAP element, the sample parts are sent to the customer for approval. They are typically stored at either the customer or supplier’s site after the product development is complete. In addition, a picture of the production parts is included in the PPAP documentation.
A master sample is the final product sample. It is inspected and signed off by the customer and the supplier.
The master sample part is further, employed to train operators and is used as a touchstone to compare production parts.
Checking gadgets and devices are employed by production. It’s a detailed list of all the tools that are incorporated for inspection, conducting tests, or measuring parts during the assembly process. Checking aids should list the part, describe the tool, and include the calibration schedule for the tool.
If there are any special customer requirements, they are recorded in this element of PPAP. Each customer lists their specific requirements for the PPAP process here.
The PPAP process is lengthy and it needs to be documented correctly. PSW, abbreviated for Part Submission Warrant, is a summary of the entire PPAP Package.
The PPAP package documents the ability of the supplier to meet all customer requirements. It also provides customers with adequate information that all areas of the design and production processes have been reviewed thoroughly. Unless stated by the customer, a PSW requires each part number to be included.
PPAP is an extensive and detail-oriented process. Let’s understand some crucial aspects of streamlining the PPAP process:
One of the ways to streamline the PPAP process is by planning proactively. If a PPAP process is planned early in the product development cycle, it’s implemented correctly and avoids changes or delays.
The next way to streamline the PPAP process is by incorporating cross-functional teams. If cross-functional teams are included in the PPAP process, they can comprehensively include distinct aspects of the process, thus ensuring that all areas are included.
Manufacturers can make use of digital tools and platforms to automate the PPAP process. In addition, all team members must be trained not only on the digital platforms but also on the requirements of the PPAP process and its best practices.
The next aspect that should be implemented by the manufacturers to streamline the PPAP process is to conduct regular audits. When PPAP documentation and processes are continually audited, potential issues can be identified earlier.
We are running several hundred parts under the PPAP process to ensure highest quality, consistently.
With our experience in handling PPAP productions we’d be happy to support you with yours. Our experienced engineers and quality specialists will guide you throughout the PPAP process.