

PMMA abbreviated for Polymethyl methacrylate is commonly referred to as acrylics. PMMA injection molding is a process where molten acrylic is injected into a cavity which upon cooling and hardening forms various types of plastic products. PMMA is applied to manufacture various plastic parts such as car windows, aquariums, and mobile phone screens. In this article, we have focused on PMMA injection molding in-depth to help you understand if it’s the best-suited material for your project.
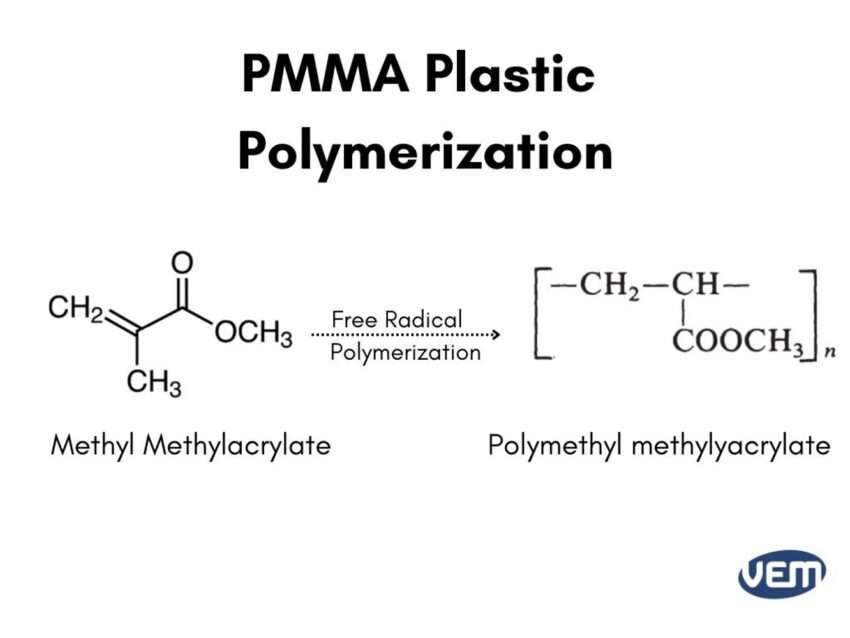
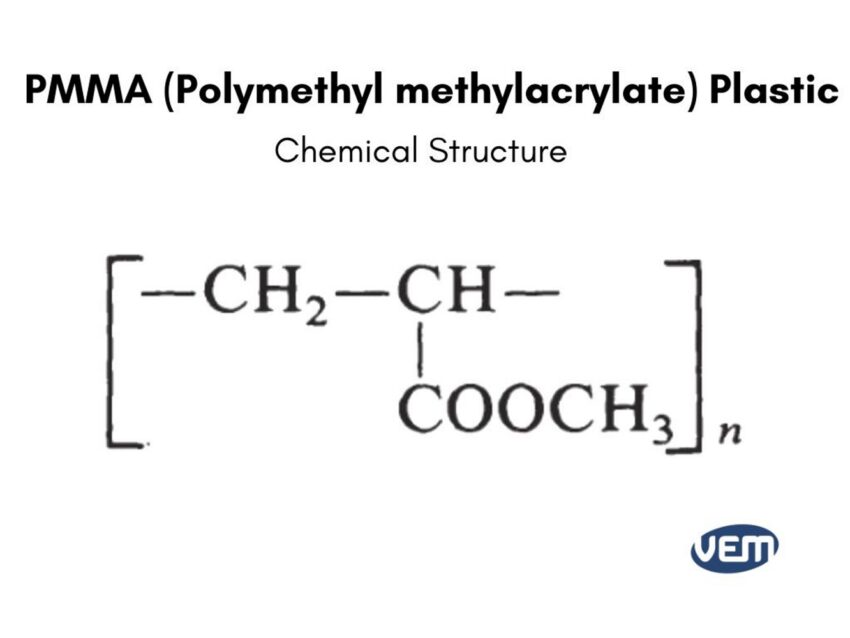
PMMA, abbreviated for Polymethyl methacrylate, is a transparent and rigid thermoplastic. PMMA is a polymer that is produced through the polymerization of monomer methyl methacrylate.
PMMA demonstrates excellent physical properties such as extensive tensile strength, great flexural strength, and transparency, like glass. One of the most prominent properties of PMMA is that it resembles glass and it is thus often used as a replacement for glass. Additionally, it is a tough plastic material and is an excellent cost-effective alternative to the less resilient glass material.
PMMA is commonly known as acrylics. Some of its common trade names are Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, Lucite, Perclax, and Perspex. PMMA sheets that are of the glass type are called Plexiglass. It is also used in high-end applications such as hip replacement and lenses for eyewear.

PMMA was first discovered by a German chemist named Otto Rohm in 1901. The PMMA discovered in 1901 was in its most novice and preliminary form and it could not be used for commercial purposes as we use it today. It thus later underwent various developments and by 1943, a more processible form of the PMMA version was developed which created a version of PMMA that can be cured at room temperature.
PMMA was processed extensively to be further developed such that it can be molded into complex shapes that are required for the biological environment. The earliest application of PMMA was in dentistry and it was later extended to orthopedics for thigh and hip replacements. Since PMMA was lightweight, easily processed, and demonstrates low toxicity, it found various applications in the medical industry. It was, however, not cost-effective and thus, restricted for a while to the medical industry.
Further developments and advanced technology developed a far more accessible and cost-effective PMMA that could be used for consumer applications. This particular development made PMMA a versatile plastic whose application spreads today, across several industries!
As injection molding developed and became more integral to manufacturing, PMMA became even more versatile and the ‘plastic of choice’ for various manufacturers! Today PMMA gets injection molded into countless products.
PMMA is also a cost-effective alternative to polycarbonate. If polycarbonate is too expensive to be applied to a project, PMMA is an excellent alternative. This is especially the case if the plastic requires a clear appearance bu not the properties of polycarbonate. There are various applications where one would prefer PMMA over polycarbonates such as jewelry, plaques, aquariums, windows, and display pieces. PMMA is comparatively lightweight and inexpensive in such cases.
In addition, PMMA has also been considered a safer option than polycarbonates as bisphenol A in polycarbonate has the potential to be hazardous.
PMMA is considered to be a better alternative to Glass. Glass is generally expensive, heavy, and can be unwieldy. E.g. iPhone screens are usually Gorilla glass and they are thus, heavy-weighted and expensive whereas various other brands use acrylic plastic for the screen displays thus, making the phones lightweight and relatively cheaper.
Acrylics are more flexible, lighter in weight, and exhibit more impact resistance than glass. They are easier to mold and fabricate according to the design specification. Additionally, Acrylics exhibit better insulation properties than glass which makes them perfect for skylights.
Acrylics can be modified according to the requirements. They are available in clear as well as various tints and colors. Acrylics can also be texturized to produce a variety of finishes. In addition, Acrylics are also incorporated with additives to exhibit a particular characteristic such as scratch- resistance or glare reduction.
Acrylics are broadly classified based on their properties. There are 2 main types of Acrylics: Extruded and Cast.

Cast Acrylic is harder than extruded acrylic and is thus, more scratch-resistant. The manufacturing process of casting is labor intensive thus, cast acrylics are more expensive. Cast acrylics are homogenous and therefore have equivalent properties.
Cast Acrylics are produced by mixing acrylic liquid ingredients in molds. During the production process, the liquid ingredients are pumped into a mold which is then submerged in warm water, and here, the polymerization takes place. Some of its properties are listed below:
Extruded Acrylics are produced through the extrusion method. Extruded acrylics are produced by pushing acrylic mass through a form thus, depending upon the direction of the flow, they have varying properties. Due to the production process, they are heterogeneous. Some of its properties are listed below:
Acrylics typically allow 92% light transmission which is greater than glass or any other plastic. This light transmission property enables the acrylics to exhibit outstanding clarity. PMMA can thus, be applied in various optical-related applications.
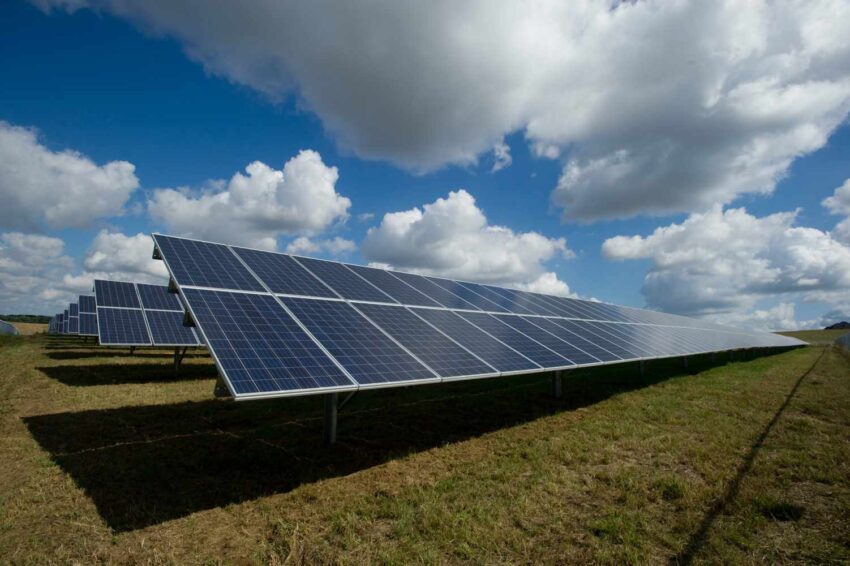
Acrylics are inherently stable to UV light which is why PMMA is used for many outdoor applications such as solar panels.

Acrylics demonstrate excellent scratch resistance. In addition, they can be processed toward featuring a glossy lustrous finish. These properties, combined with PMMA’s dimensional stability, enable its use in many different applications, such as automotive body parts, furniture, or kitchen. Additionally, acrylics are more scratch-resistant than any other glass product. In this manner, the molding process generates products that can maintain their lustrous appearances for a long time without degradation.
Acrylic has a density of 1.185 g/m3 – 0.00185kg/m3 whereas glass has a density of 2.4 g/m3 – 0.0024kg/m3 thus, PMMA plastic molding produces lightweight products and is an excellent alternative to glass.
PMMA can be molded into developing complex designs. PMMA injection molding process can reproduce a significant number of complex products that are identical in terms of shape, size, and weight.
Acrylics can be mixed with resins to create a wide variety of colored products. It can be further modified to improve a specific property. This is generally achieved by incorporating additives. These modifications are typically performed
es of the polymer, usually targeted toward specific applications. Examples of the properties that can be adjusted in this way are impact resistance, chemical resistance, light diffusion, UV light filtering, or optical effects.
The manufacturing process of acrylic products can release highly toxic fumes thus, it needs to be handled with precaution. Anyone who is handling acrylic sheets should be provided with appropriate protective equipment and clothing. If not handled properly and the right precautions aren’t taken, acrylics could blow up during polymerization.
PMMA has unique properties such as low density, biocompatibility, UV resistance, easy molding, and delivering aesthetics while being cost-effective. PMMA has thus become a popular biomaterial for dental applications. It is commonly used for prosthetic dental applications such as the fabrication of artificial teeth, denture bases, dentures, orthodontic retainers, and crowns, and the repair of dental prostheses.
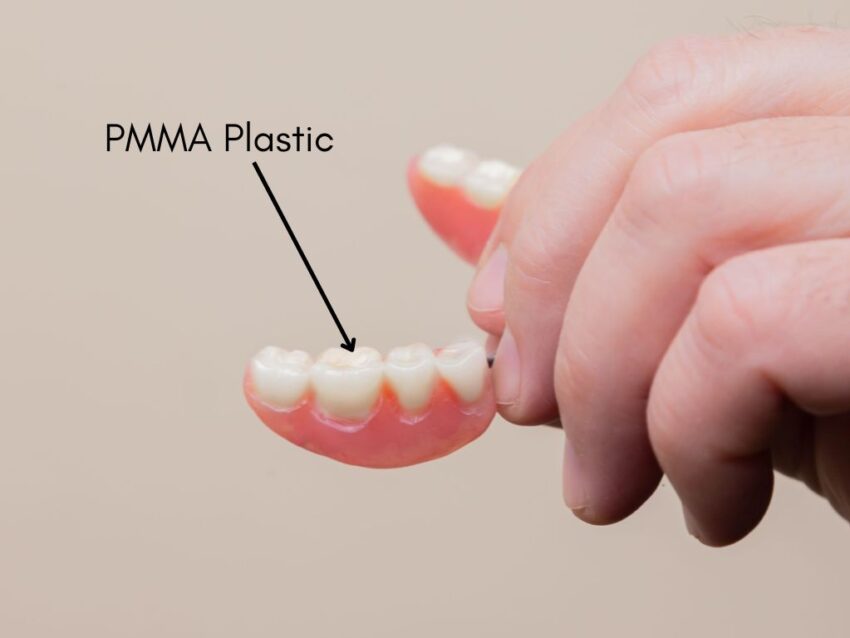
In addition to prosthodontic applications, PMMA can be applied to a wide range of medical applications such as diagnostics, and incubators.
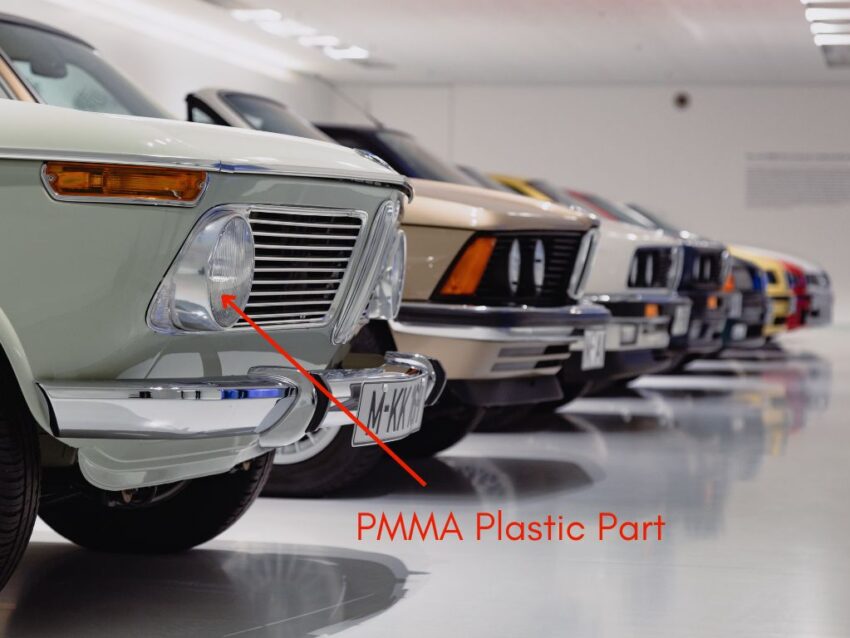
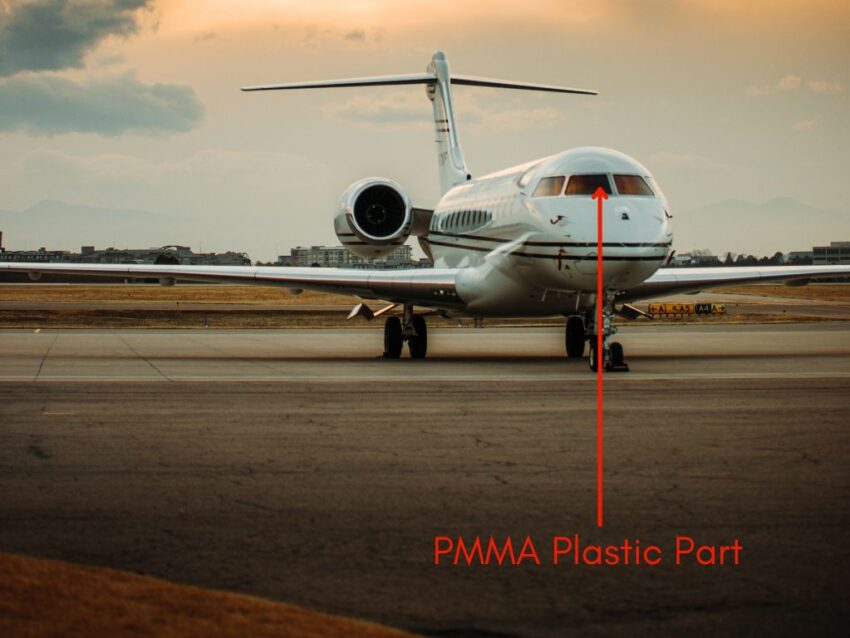
PMMA grades are known for their transparency! It allows 92% of the light to pass through, which is more than glass or any other plastic. This outstanding clarity makes it an ideal plastic of choice for various applications in the automotive, aviation, and marine industry such as rear lights, windshields, and plane windows.
PMMA provides excellent optical clarity, light transmission, and color accuracy which is why it is extensively used in exterior, rear, and indicator light covers of the automotive.

Since PMMA is lightweight and resistant to salt and cleaning products, it is extensively used for manufacturing windshields and windows. PMMA is also used for windscreens, windows, and canopies in airplanes as it can resist high inside cabin pressure and harsh UV radiations.

PMMA has unique properties for the construction industry such as optical clarity and UV resistance. It is an ideal material for construction applications such as sound barriers, facades, aquaria, and greenhouses. PMMA also has high mechanical resistance and its reliability enables architects to build beautiful architectural monuments.
Acrylic is one of those rare plastics that combine high-performing characteristics with beautiful aesthetics. The aesthetics can be customized according to the designers in the form of color, finishes, and effects. In addition to the furniture and design industry, acrylics are a popular plastic of choice for manufacturing photo frames, clear table tops, and storage plastic parts.

PMMA exhibits excellent optical clarity, high light transmittance property, surface hardness, and scratch resistance which are important properties for electronics that would be used on a regular basis. Due to these properties, acrylics are widely applied to manufacture LCD screens, TV, and mobile phones.
Photovoltaic modules of solar panels are continually exposed to harsh environmental extremes such as sunrays and rain. Thus, the solar panels undergo constant stress which is why acrylics are a popular choice for photovoltaic solar modules. PMMA is durable, can withstand stress, and is weather-resistant which is why it is the perfect economical choice for solar applications.
The methyl acrylate monomer is polymerized through free radical chain polymerization for the formation of PMMA
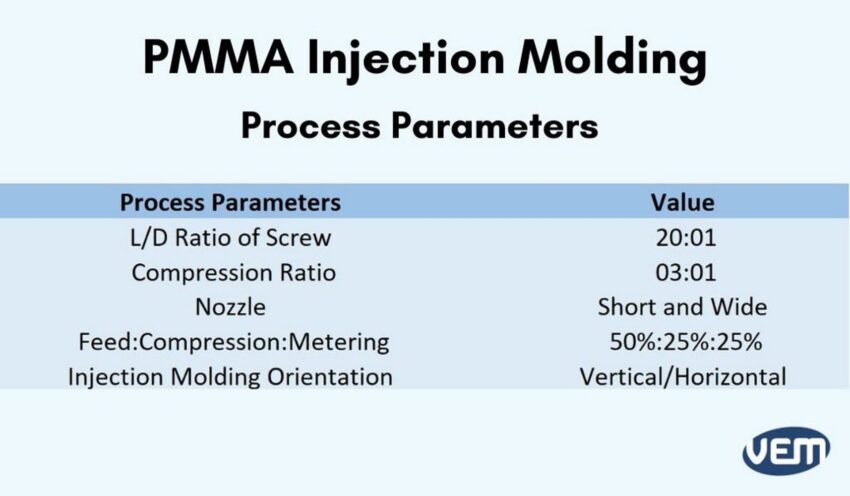
PMMA beads or pellets which are usually the starting material should be free of solvents to avoid the formation of bubbles. This is achieved by drying. PMMA Injection molding is the same process as conventional injection molding:
Acrylics have a water absorption rate of 0.3-0.4%. For injection molding, it should be below 0.1% of the temperature i.e. usually 0.04%. The presence of water leads to air bubbles and the formation of airlines thus, PMMA resins need to be dried well before introducing them into the barrel.
The drying temperature is usually set at 80-90°C / 176-194°F for 3 hours.
The thermal stability of PMMA injection molding is medium and the thermal decomposition temperature is slightly higher than 270℃ / 518°F. For screw-type injection molding machines, the barrel temperature should be controlled at 180 – 230℃/ 356 – 446°F.
The cooling rate of acrylics is fast thus, the plastic parts are easily stressed. The high and low control of injection mold temperature should be strictly maintained to avoid this. The general injection mold temperature should be controlled at 40-80℃ / 104 – 176°F.
Since the viscosity of PMMA melt is high and the flowability is poor, the injection pressure should be maintained high at 80-120 MPa / 11603-17404 Psi. The holding pressure is 40-60MPa / 5801-8702 Psi.
VEM Tooling has the expertise for your PMMA injection molding project. At VEM Tooling, we ensure that receive a great experience and dependable service! To better understand how VEM tooling can serve you for your PMMA injection molding project, contact us or request a quote today.
Acrylics are not only cost-effective but also more durable than glass. It demonstrates more impact resistance than glass (Usually 10X more). Additionally, Acrylics offer a lustrous shine and a glossy finish!
Acrylics are not toxic in their final forms but during production, their manufacturing process releases minute amounts of toxic fumes. Comparatively, the production of toxic fumes is not the same as other materials. Acrylic is classed as non-hazardous under OSHA regulations as it is one of the few materials that has very low toxic fumes released during its production and the final form is free of toxicity.
Acrylics do not turn yellow in the sun. Acrylics are also not affected by UV rays. They are thus ideal for shed windows and colored skylights. They are also popularly used for panels in home projects.
Acrylics are weather resistant which means they are durable and can withstand storms, winds, and heavy rains. There is no degradation in transparency which is why the clarity also remains the same, unlike glass.
Acrylics are clear like glass but they don’t look like glass in terms of the finish.
Acrylics aren’t scratch-resistant. Acrylics scratch more than often but in most cases, they can be polished.