

The injection molding industry applies a wide array of plastics for various projects however; when it comes to the medical industry, it is imperative to understand the concept of medical-grade plastic materials. In this article, we have explained in detail medical-grade plastics and their various types.
Medical-grade plastic refers to plastic materials that are used to design and manufacture medical-grade products. Medical grade plastics are applied to manufacturing specifically medical products such as MRI casings and plastic syringes.

They are generally the type of plastics that are considered to be suitable for making medical devices. Their suitability is attributed to biocompatibility which is especially imperative in medical components as they come in contact with the human circulation system.

In addition to medical devices, medical-grade plastic material is also applied to manufacturing products for in vitro diagnostics and as primary packaging for pharmaceuticals.
Every medical-grade plastic has properties that may be similar to other polymers but what sets them apart is their ‘biocompatibility’. Biocompatibility is when a plastic material is compatible with living tissue without causing any type of toxic or immunological response when exposed to the body.
In addition to being biocompatible, medical-grade plastic should be malleable, hard, precise, and compatible with injection molding and 3D printing processes.
There are certain properties that make medical-grade plastics safe for manufacturing medical components. These properties are primarily responsible for safety. They range from demonstrating biocompatibility, non-permeability, and hardness to chemical and heat resistance. Let’s take a look at how these properties benefit:
Today, plastic polymers are increasingly becoming a popular choice over metals. Let’s take a look at some of the properties that make manufacturers choose plastic polymers over metals:

Plastic polymers have some inherent properties as they are durable, chemical resistant, and heat resistant. They can thus withstand constant sterilization which is suitable for manufacturing medical components.
Some plastic polymers exhibit greater hardness and tensile strength than metals such as Nylon which has a high tensile strength of 12400 psi / 85.5 MPa.
Plastic polymers are compatible with several manufacturing processes. They exhibit high machinability. Some of the common manufacturing processes include injection molding, 3D printing, and blow molding.
Most medical thermoplastics are recyclable. Thermoplastics can be remelted and reshaped without them losing their molecule integrity thus, they can be recycled effectively. This way, unused parts can be reused during manufacturing which reduces material wastage and improves cost-effectiveness. An example of this feature would be polypropylene which can be melted under heat and is shapeable using any manufacturing process.
This property of thermoplastics is unique whereas other materials such as glasses and metals need proper disposal methods. Thus, thermoplastics are a cost-effective manufacturing process.
Medical plastic polymers are highly moldable into different shapes. They are thus very versatile! Due to their versatility, medical-grade plastic polymers are suitable for making various medical parts such as bedpans, inhalation masks, IV tubes, and catheters.
The material cost of plastic polymers is generally low, and the manufacturing cost of large-scale production makes them extremely economical. Additionally, their low cost makes them suitable for manufacturing products for one-time use.
Their inherent properties of being corrosion resistant, shatterproof, and biocompatibility are like metal and glass thus, the health industry can reduce manufacturing costs, and in turn, the patients can benefit from the same health care services at lower costs.
USP abbreviated for U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention is a body that dictates the testing for plastic medical devices to evaluate biological responses. USP is recognized in 140 countries and its standards are enforceable by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
You should note that there are no FDA-approved plastics for medical devices. As the plastic parts are being manufactured for the medical industry, the entire product, part or device is tested. This is because there are many manufacturing variables that can alter the properties of the material.
Each USP device class is based on the duration of use and the application, thus requiring a different level of regulation and compliance. The below diagram depicts the various level of USP classes:
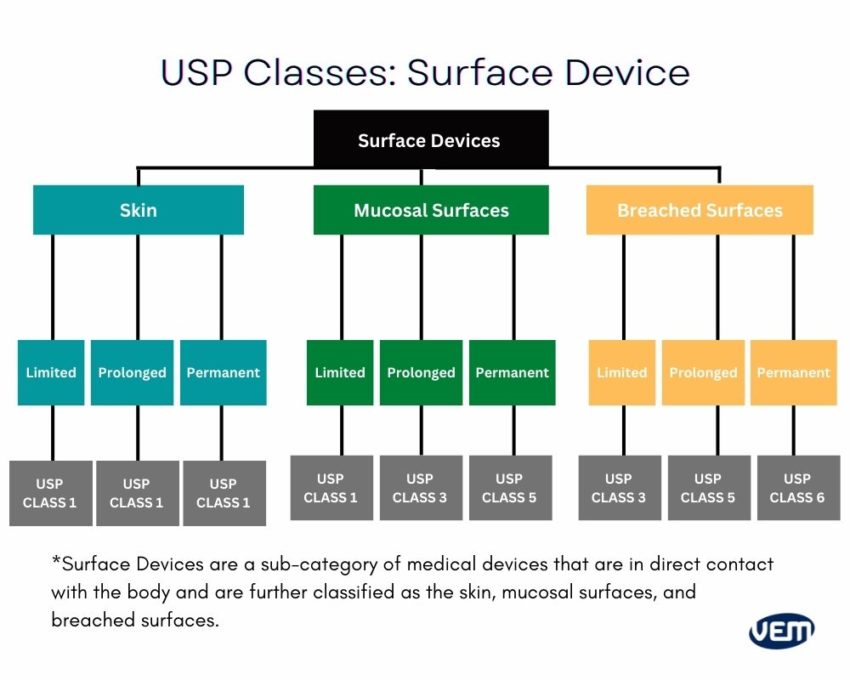
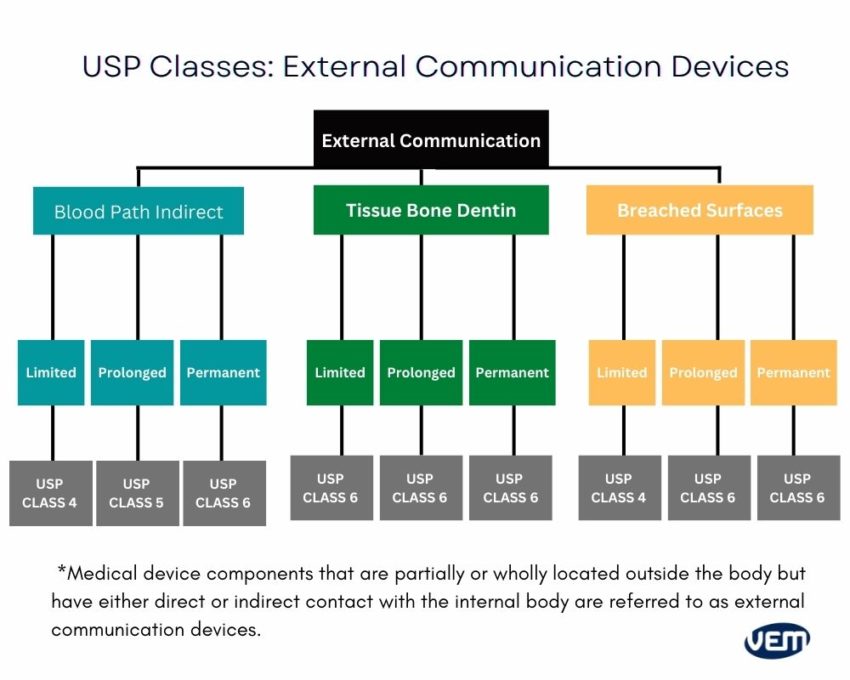
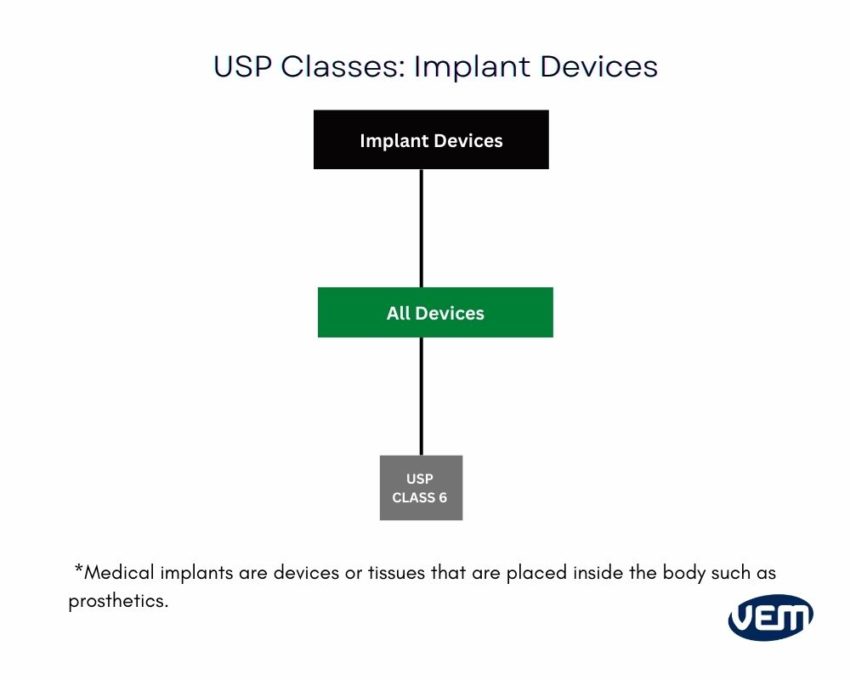
Medical-grade plastic materials should always be handled in cleanrooms. It is imperative as medical devices are built for the human circulation system or to be used in healthcare settings and thus, there cannot be any contamination.
Cleanrooms play a vital role from the processing of medical grade plastics to manufacturing medical devices and ensuring that the products meet the necessary regulatory standards.
The cleanroom for medical device manufacturing is typically between ISO 5 (Class 100) to ISO 8 (Class 100,000) cleanroom. The following image showcases apparel requirements that one needs to adhere to while entering a clean room:
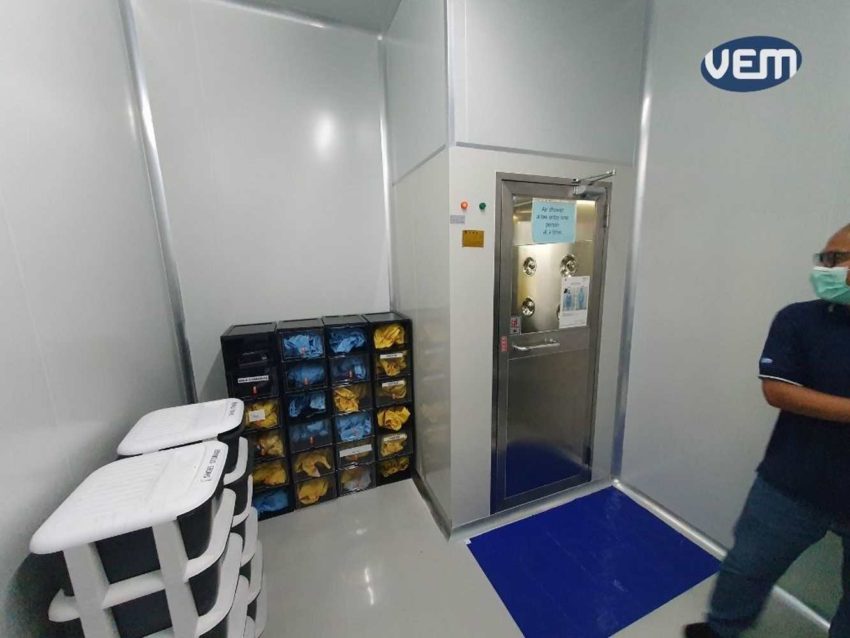

If you like to learn more about cleanrooms, you can check our in-depth article explaining the requirements of injection molding in a cleanroom.
The ISO 10993 is a type of certification that verifies the biocompatibility of a medical device. ISO 10993 certification evaluation also extends to constructing the medical plastic polymer and other materials such as additives, packaging, and degradation products.
From the above classes, Class VI undertakes rigorous testing for plastic components for medical devices. Class VI standards indicate that the product must exhibit a very low level of toxicity. The ISO standard also includes the risk management of medical devices.
Risk analysis requires identifying and characterizing all the materials that have the potential to be in the final medical device. This also includes analyzing any manufacturing additives and an examination of the processing impact that can take place on material composition and chemistry. The risk assessment includes the following factors:

There are various types of plastic polymers but the ones that are most commonly used for medical injection molding are thermoplastics. Thermoplastics are plastic polymers that soften upon heating and harden upon cooling. We have listed some of the most commonly employed thermoplastics in medical injection molding:
PE, abbreviated for Polyethylene is a plastic polymer with a linear structure of monomeric ethylene that is formulated in high or low densities. PE has many variations such as high modulus polyethylene, high-density polyethylene, cross-linked polyethylene, and low-density polyethylene.
Polyethylene is one of the top medical-grade plastics. Its properties are impact resistance, corrosion resistance, and solid structural integrity when exposed to frequent sterilization cycles. It is biologically inert and non-degradable in the body which is why it is often applied in making prosthetics.
PMMA, abbreviated for polymethyl methacrylate, is produced from methyl methacrylate. It is rigid, tough, durable, UV-light resistant, and has an excellent light transmission property. Additionally, It is also chemical resistant and has a high melting point at 200-250°C / 392-482℉.
PMMA is a popular medical-grade plastic for making endoscopic medical parts.
PVC abbreviated for Polyvinyl chloride is a medical-grade plastic polymer that is made by chlorinating PVC polymers. PVC is known for its versatility and is a rigid, flame and, chemical-resistant polymer.
There are 2 types of PVC plastic that are used to make medical plastic products. These are listed below:
Both types of PVCs are suitable for manufacturing medical devices for hemodialysis, tubing, cardiac catheters, and artificial limb materials.
PC abbreviated for polycarbonate is made by condensing bisphenol A and phosgene. It is a strong plastic polymer that is tough, flame retardant, shatterproof, and abrasion-resistant. Polycarbonates are highly transparent and are thus a great alternative to glass.
It’s also sterilizable using steam at 120°C / 248℉, gamma radiation, or chemicals. It also exhibits high strength, good heat resistance, and biocompatibility thus, they are applicable in making medical components such as IV connectors that are used in renal dialysis and cardiac surgery.
PP, abbreviated for Polypropylene, is a white, rigid, and chemically resistant polymer that is produced by chain-growth polymerization of propylene and ethylene. This medical-grade polymer plastic is resistant to stress, cracking, impact, and fatigue.
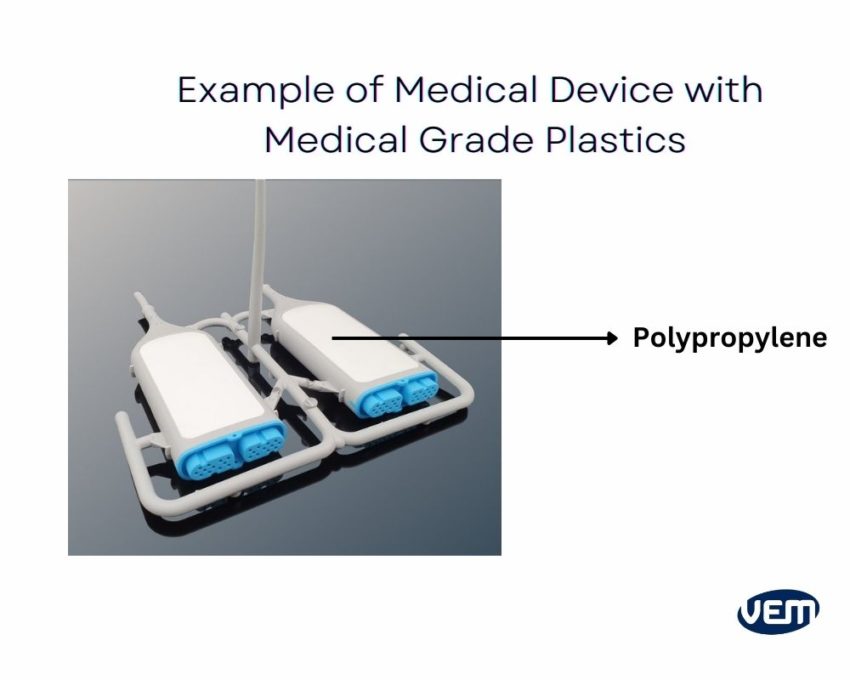
It also has a high melting point of about 1710℃ / 3110℉. Due to its high temperature, it provides enough resistance while sterilizing in the autoclave. Therefore, it is applicable in making medical plastic components such as disposable syringes, oxygenator membranes, prescription bottles, and finger-joint prostheses.
Polyamide is produced by linking amino groups to carboxylic groups. It can be either natural or synthetic (Nylon variations). Polyamides or Nylon are known for their flexibility, tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and anti-corrosive properties.
It is manufacturable through various processes such as CNC machining, injection molding, and 3D printing. Polyamide medical parts examples include stent delivery systems and prescription bottles.
ABS plastic is abbreviated for Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and is made by polymerizing styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. ABS has high tensile strength, high abrasion resistance, chemical resistance, and anti-corrosive properties.
Just like Polyamides, it’s compatible with various manufacturing processes such as injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion. ABS is highly rigid and it is thus preferred in the medical industry for making non-absorbable sutures and tracheal tubes.
Medical-grade plastic polymers are applied to various projects such as plastic gloves, plastic syringes, and other surgical tools. When compared to conventional plastic polymers, they differ in terms of biocompatibility. To select the right plastic material for your medical product, reach out to us.
There are various types of medical-grade polymers, and it might be challenging to choose the right one for your project. VEM Tooling has the expertise for your medical injection molding project.
At VEM Tooling, we offer dependable services and ensure that you have a great experience. To better understand how VEM tooling can serve you for your medical injection molding project, contact us or request a quote today.