

Today, Polyethylene is one of the most sought-after thermoplastics in the injection molding industry. Polyethylene is a popular injection molding material in the manufacturing industry due to its affordability, machinability, and compatibility with other materials.
It is applied to various industries and can be categorized into several subcategories. The sub-categorization of polyethylene plastic is based on its molecular structure and each of which demonstrates certain unique characteristics that make it suitable for use in particular applications. The most common types of polyethylene are
Among the above 5 forms of polyethylene, the two most common kinds of PE are high-density polyethylene (HDPE) and low-density polyethylene (LDPE). In this article, we discuss everything you need to know about these two materials, so you can decide which type of polyethylene is best for your next project.
LDPE, abbreviated for low-density polyethylene, is a soft, flexible, and lightweight translucent plastic.
Low-density Polyethylene is a chemically inert and semi-rigid polymer with low levels of crystallinity at about 50-60%. It is known to demonstrate excellent physical properties such as flexibility, chemical, and impact resistance. Additionally, LDPE is also stain-resistant, electrically insulating, and waterproof.
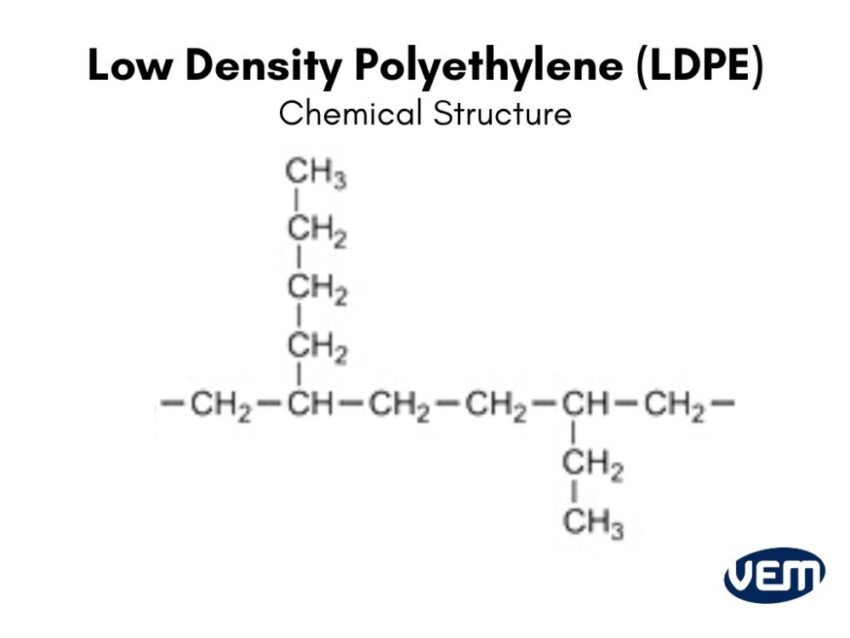
LDPE is a branched version of polyethylene. It is produced through a single monomer, ethylene which makes it a homopolymer.
The chemical structure of LDPE includes many short branches and is composed of 4,000-40,000 carbon atoms. Its molecules are more loosely packed than other variants of Polyethylenes. It’s still durable and strong but it is less dense than other linear polyethylenes such as HDPE. You should note that LDPE has a higher degree of short and long-side-chain branching.
The above image is a cross-sectional picture of a vacuum void formed at an area where the outer section of the plastic has a small support ridge.
| LDPE | HDPE | |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | 105 – 115°C / 221 – 239°F | 135°C / 275°F |
| Tensile strength | 1,400 psi / 9.65 MPa | 4,000 psi / 27.47 MPa |
| Tensile elongation | 500 psi / 3.44 MPa | 600 psi / 4.13 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | 30,000 psi / 206.84 Mpa | 200,000 psi / 1378.59 MPa |
| Water Absorption rate | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion |
| Density | 0.910–0.940 g/cm3 / 910-940 Kg/m3 | 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3 or 970 kg/m3 |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.12 – 0.70 | 0.200 – 0.280 |
LDPE has various benefits, but it also has some drawbacks. We have listed some of the limitations below:
LDPE is widely applied to manufacture packaging material for various industries. Some of the most popular applications include toys, grocery bags, plastic films or wraps, flexible packaging material, and food and beverage containers.
Since its lightweight, LDPE is commonly used to manufacture light-packaging materials such as six-pack rings for canned beverages, waterproof carton lining, and plastic wraps.
Low-density polyethylene is also used to manufacture water pipes and hoses for the pipes and fittings industry due to its plasticity and low water absorption.
HDPE, abbreviated for high-density polyethylene is also referred to as Polyethylene High-Density (PEHD), alkathene, polythene, and #2 plastic. It is a thermoplastic polymer made from petroleum and it offers greater rigidity and durability than LDPE.
HDPE exhibits an outstanding tensile strength and is known for its large strength-to-density ratio. HDPE plastic also has a high-impact resistance and a relatively high melting point compared to other polymers.
It is also a highly adaptable plastic and can be applied to a variety of industries that ranges from pipes to storage bottles.
HDPE has a linear structure as the branching degree is relatively low when compared to other categories of polyethylene. It’s a polymer made up of repeating units of ethylene monomer, and its chemical formula is (C2H4) n.
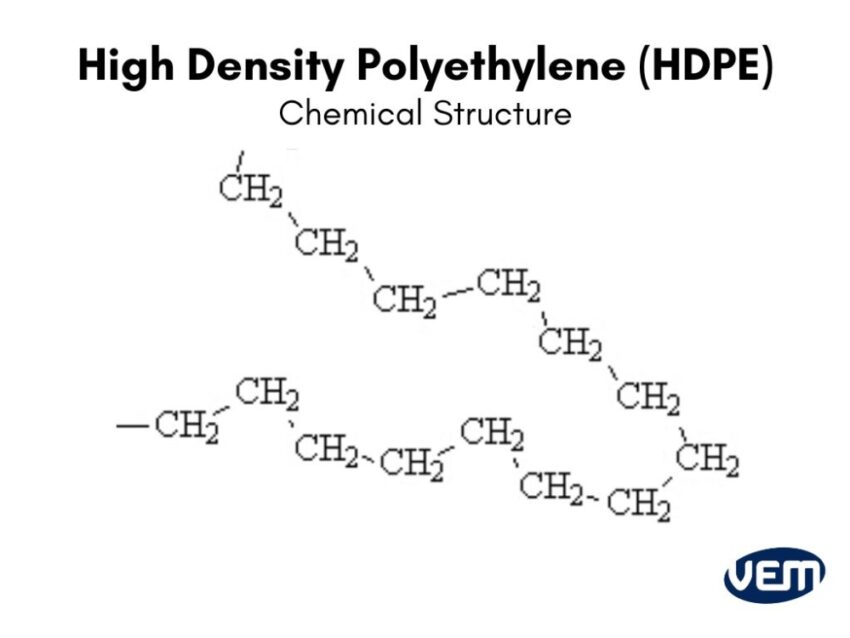
Since its molecules are packed together tightly, HDPE is an extremely strong material with high tensile strength, rigidity, and impact resistance.

| LDPE | HDPE | |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | 105 – 115°C / 221 – 239°F | 135°C / 275°F |
| Tensile strength | 1,400 psi / 9.65 MPa | 4,000 psi / 27.47 MPa |
| Tensile elongation | 500 psi / 3.44 MPa | 600 psi / 4.13 MPa |
| Flexural modulus | 30,000 psi / 206.84 Mpa | 200,000 psi / 1378.59 MPa |
| Water Absorption rate | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion | 0.10% over 24-hour immersion |
| Density | 0.910–0.940 g/cm3 / 910-940 Kg/m3 | 0.93 to 0.97 g/cm3 or 970 kg/m3 |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.12 – 0.70 | 0.200 – 0.280 |
HDPE is susceptible to stress cracking under intense pressure and low-to-moderate heat resistance.
HDPE has a linear structure, which makes it an ideal material for applications that require high-tensile strength such as vehicle fuel tanks, boat parts, pipes, and tubing.

HDPE is malleable and due to its dimensional stability, it is often used in outdoor equipment such as playgrounds.
HDPE is also applied in various industrial projects such as pipes, tubings, and chemical tanks. It is also applied to various consumer goods such as food and beverage bottles, and cutting boards. It is also used in applications that require a strong packaging material such as bottle caps, plastic milk bottles, drums, and bulk containers.
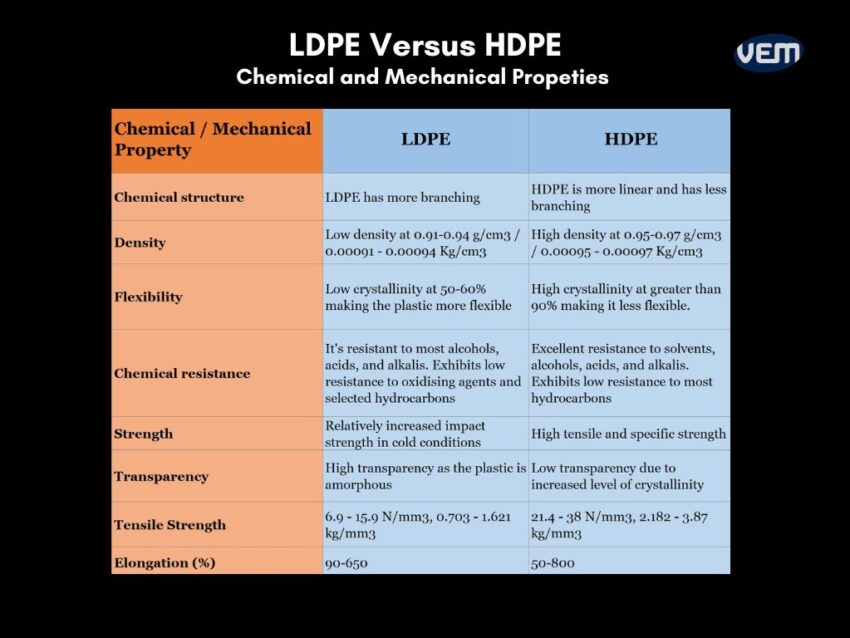
HDPE and LDPE are the two most common polyethylenes that have similar properties with differing structures. HDPE has a linear structure and is opaque, while LDPE is a relatively transparent, branched version of PE.
Both materials demonstrate excellent strength, weldability, impact, and chemical resistance.
Although both, LDPE and HDPE are derived from the same ethylene monomer, they demonstrate a wide variety of unique properties due to the difference in their chemical structure.
As the name suggests, low-density polyethylene (LDPE) has a lower density, strength, and temperature resistance whereas high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is characterized by higher specific strength and heat resistance.
The table below depicts the various differences between LDPE and HDPE:
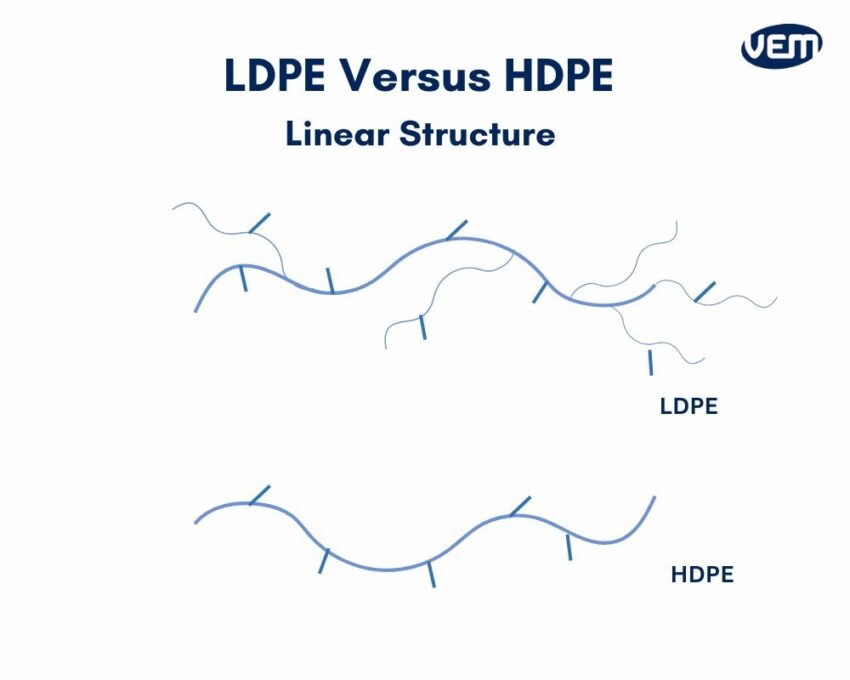
The linear structure of LDPE has more branches whereas that of HDPE is packed together more tightly which is the reason for its impressive material characteristics.
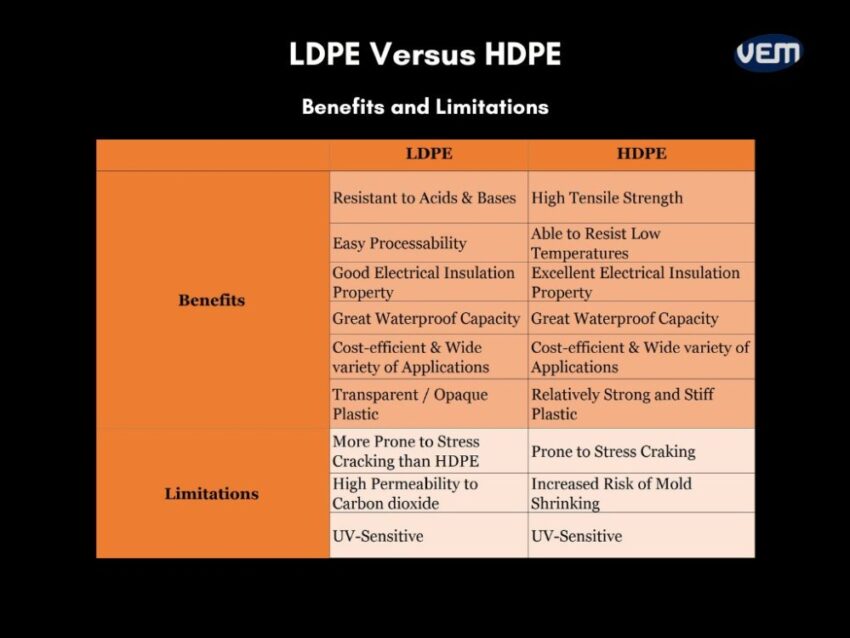
Both materials have various benefits but they also have some limitations. The table below depicts the benefits and limitations of using LDPE and HDPE:
LDPE and HDPE can be processed through injection molding and additive manufacturing techniques however; they are both best suited for different techniques. LDPE is best suited for injection molding and HDPE is best-suited for CNC machining as it helps to achieve tight tolerances.
It’s imperative for the product teams to research and determine the best-suited material for your upcoming project. A trusted manufacturing partner can guide you to make the most optimum decision for your project.
LDPE is produced at a high pressure of 1000-3000 bar at 80-300°C via a free radical polymerization process.
LDPE is manufactured either through a stirred autoclave or a tubular reactor. Its manufacturing process includes ethylene gas compression, material polymerization using an initiator, and gas separation.
HDPE can be produced either through slurry polymerization or gas-phase polymerization. The process starts with polymerization from a solution of ethylene monomers, followed by separation and drying. HDPE is made through a 3-step process which is listed below:
Once LDPE and HDPE are produced, they can be processed through either of the following methods:
Injection molding is an efficient manufacturing process that converts LDPE and HDPE resins into plastic parts that are defined by the mold.
Plastic resins are sent to a hot barrel, in which the resins melt through a screw barrel and heater bands. The plastic resins melt here, which is further injected into a pre-designed mold. The material also cools down here, and after solidifying, the plastic material is ejected out of the molding machine.
Extrusion is similar to injection molding that is conducted by incorporating heat to melt the plastic granules. The only difference between extrusion and injection molding is at the end, where the melted resins go through a pre-designed opening and are then cooled down to solidify.
Blow molding is often applied to manufacture hollow-shaped plastic goods. Instead of injecting the molten plastic, the process uses compressed air to blow the material into the mold.
Understanding the difference between LDPE and HDPE is imperative as it can help you choose the best material for manufacturing your plastic part. If you have any queries about LDPE, HDPE or any other type of polyethylene, you can reach out to us. VEM Tooling has the expertise for your PE injection molding project. Our team has an experience of over 20 years with manufacturing and mold making. We can surely help you to make an optimum decision for your project.
The molecules are tightly packed together during crystallization, making HDPE dense and possessing higher resilience than LDPE.
HDPE is an ethylene-based polymer plastic that is created by processing petroleum under extreme heat and pressure.
Yes, HDPE is appropriate for waterproofing projects.
OTR, abbreviated for oxygen transmission rate, is the steady-state rate at which oxygen gas permeates through a film at specified conditions of temperature and relative humidity. The values of OTR are expressed in cc/100 in2/24 hr in US standard units and cc/m2/24 hr in metric (or SI) units.