

Selecting a manufacturing process for creating and producing parts is a very critical decision! The product designer and engineer must analyze various parameters such as cost, speed, and accuracy to maximize profits and ensure the overall performance of the operations. This analysis needs to balance the technical factors and the operational costs. When we are selecting manufacturing technologies to produce parts or create prototypes, CNC machining, and 3D printing have proved to be extremely beneficial for manufacturers. They both have their merits and the right choice depends on a plethora of factors!
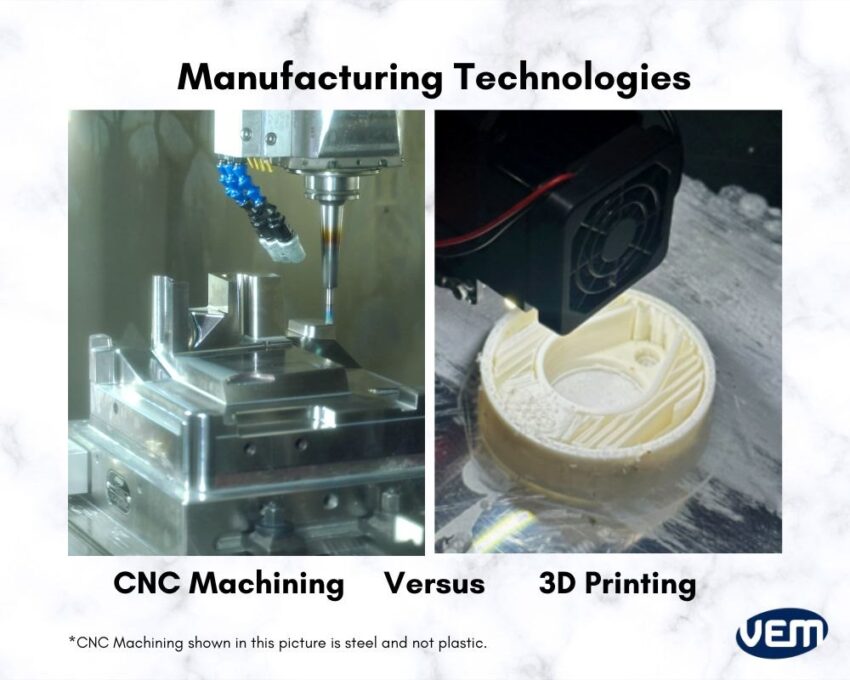
If you are deciding between CNC Machining and 3D printing, then there are various considerations and constraints. In this article, we discuss the two techniques in detail and some of the important factors that can help you decide between these two technologies for your operations and business.
CNC manufacturing, abbreviated for computer numerical control, was first introduced in the 1940s and is today, one of the most pre-eminent manufacturing technologies!
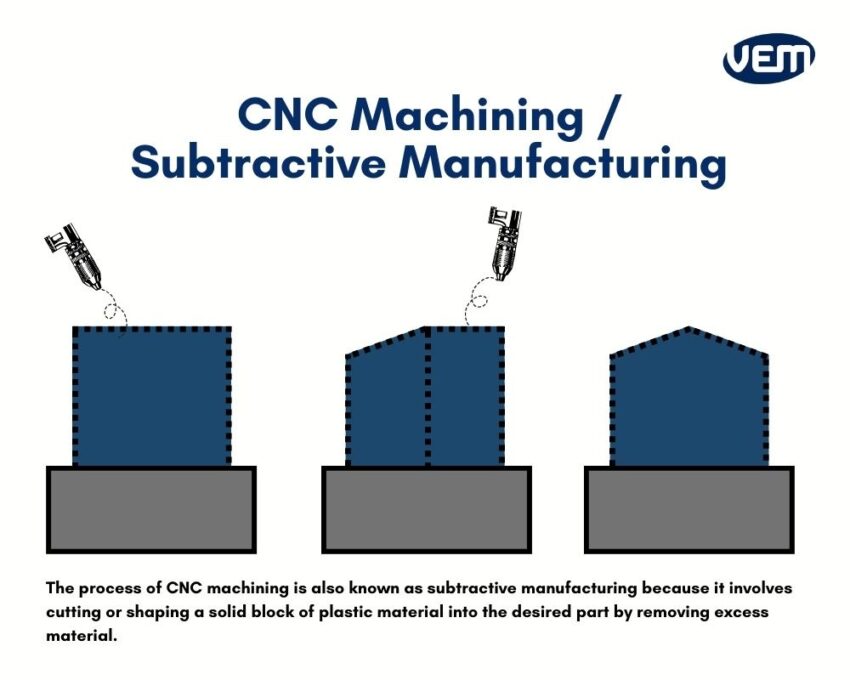
CNC machining is a term that describes the manufacturing process of milling and turning. CNC machining is also known as subtractive manufacturing and is widely used as a tool to machine highly complex parts that need to be optimally precise! Today, CNC machining or subtractive manufacturing is available in various forms such as milling, turning, laser cutting, wire EDM, and carving.
The process of CNC machining is known as subtractive manufacturing because it involves cutting or shaping a solid block of plastic material into the desired part by removing excess material. This process is carried out with the help of a CNC machine that includes a computer
and a variety of extremely sharp rotating cutters.
The computer in the CNC machine gauges the required movement of the cutting tool and this produces accurate results! The process starts with the CAD model and the data of the model is then translated into either G-codes or M-codes by the computer. These codes are specialized languages that signal the CNC machine to further create the desired shape of the part.
CNC machining is beneficial as it increases the production speed and efficiency. It thus has various applications in production.
3D printing, also referred to as additive manufacturing, was recently introduced in the 1980s and is relatively a new fabrication technique that involves creating a part layer by layer through a printer controlled by the computer. It is also referred to as rapid prototyping since it can develop physical prototypes through digital designs very quickly.
The 3D printing technique is extremely advantageous for the manufacturing industry due to its speed, and flexibility. Since its invention, the 3D printing technique has significantly evolved due to advancements in technology and materials. You can read more about the role of 3D printing in manufacturing here.
The 3D printing process is simply the opposite of CNC machining. In this technique, the material is added rather than being removed. It deposits material on the build platform layer by layer and is capable of working with various types of materials.
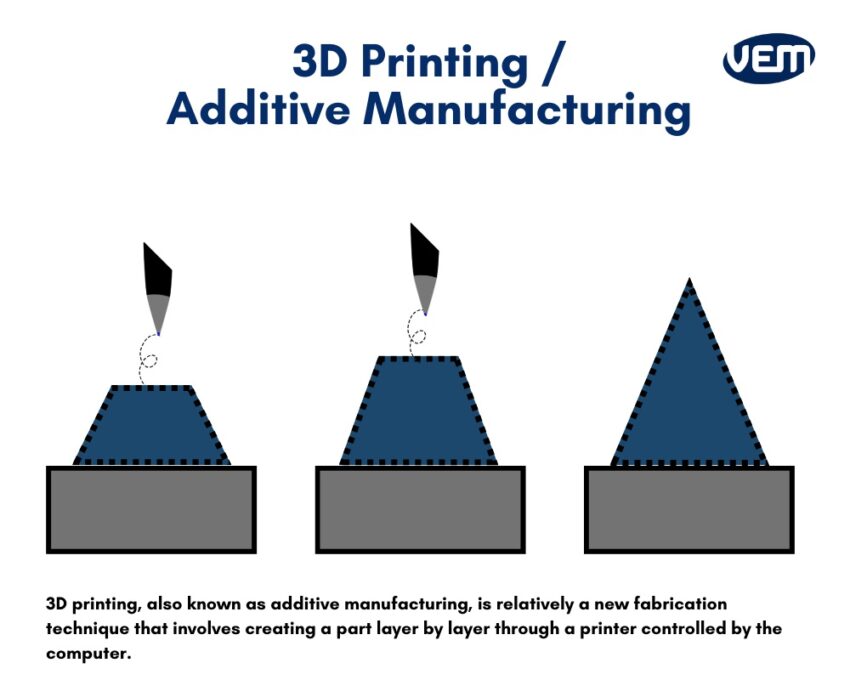
Since additive manufacturing techniques create sections in layers, it enables versatility, which is generally a limitation of other techniques.
3D printing is a flexible manufacturing technology that enables manufacturers to choose the material, speed, finish, and other technical factors. Some of the most common techniques in 3D printing are listed below:
There are various factors to consider when choosing a manufacturing technology that’s optimal for your specific application. In most cases, the end results are similar, but CNC machining and 3D printing operate in different ways. In this section, we discuss some factors that you must consider for selecting either 3D printing or CNC machining for your project.
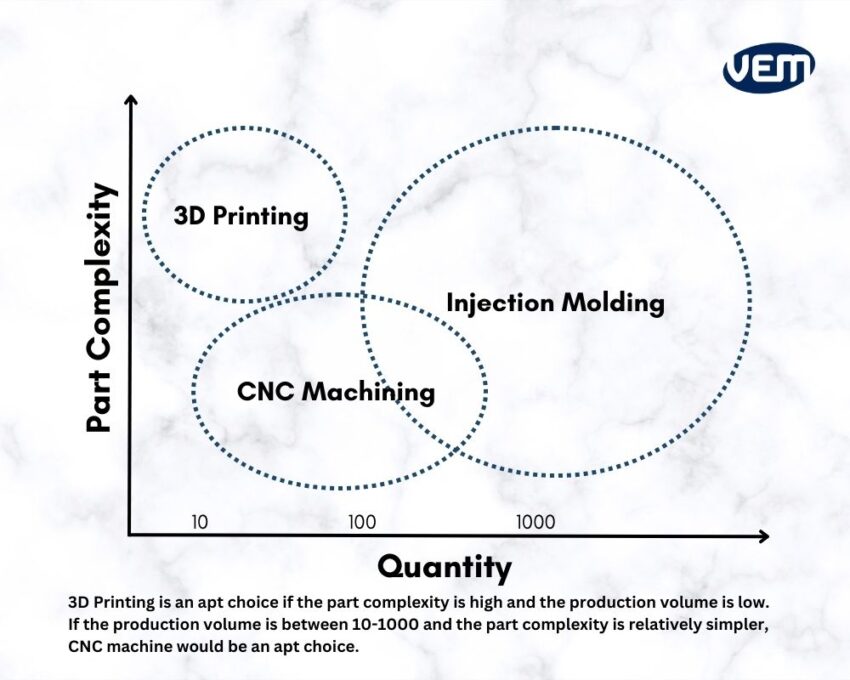
The first factor that you must consider when choosing between 3D printing and CNC machining is the number of parts that you need to manufacture. You should note that other factors such as materials and part geometry also influence this decision!
It’s typically a thumb rule that if a particular part has relatively simpler geometry, it should be made via CNC machining. In addition, CNC machining is cheaper for larger quantities and if the quantity is extremely low i.e. below 10, then 3D printing should be considered. It is also faster as well, especially for simpler geometry parts.
The following table enlists the number of parts and the type of technique you should choose accordingly for your part.
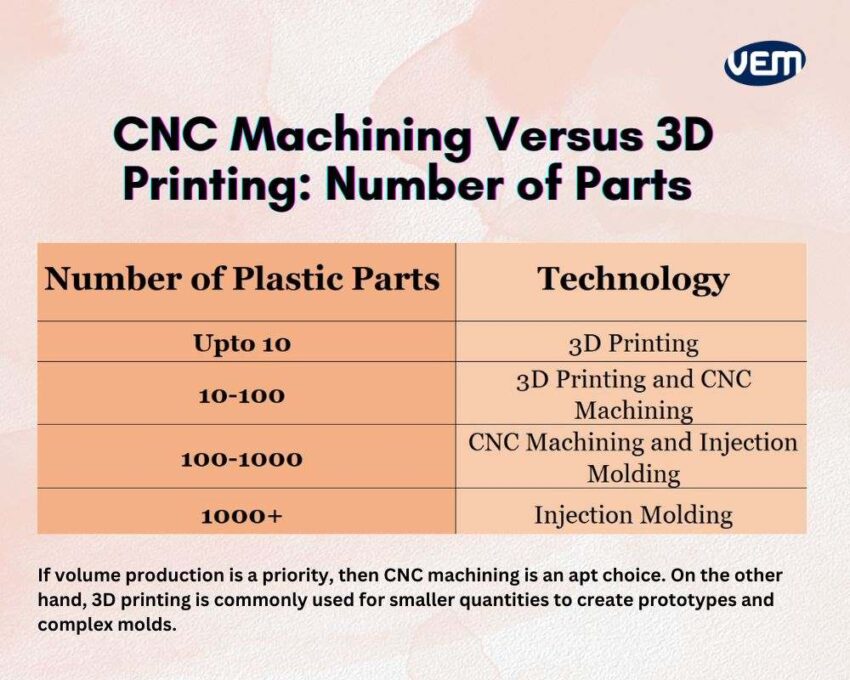
Typically, the larger the production volume, the more cost-effective the process has to be. If volume production is a priority, then CNC machining is an apt choice. On the other hand, the 3D printing technique is commonly used to create prototypes and complex molds.
The next factor to understand is which technique offers better dimensional accuracy! CNC machining is repeatable and offers tighter tolerances. It is able to provide better dimensional accuracy than 3D printing especially, in the case of components that need to demonstrate mechanical strength.
Most of the cutting tools in CNC machining have internal corners with a radius and external surfaces with sharp edges. They are thus able to machine very thin and accurately which is why it is apt for parts that are large as well as small. CNC machining is one of the best options for manufacturing precise components in medicine and aerospace industries as it exhibits infinitesimal to no margin error.
In the case of 3D printing, there are various systems and they offer different dimensional accuracy. You should note that industrial 3D printers produce parts with very good tolerances but the maximum part size is relatively smaller, and this is because 3D printing requires strict environmental control. The below table indicates the tolerance level as per the technology.
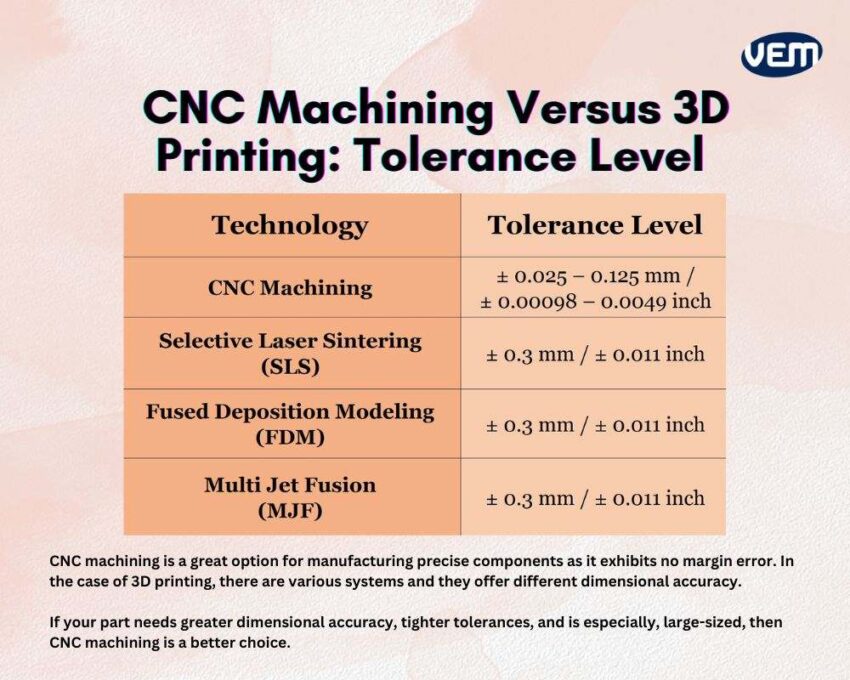
If your part needs greater dimensional accuracy, tighter tolerances, and is particularly large-sized, then CNC machining is a better choice.
Material considerations are one of the major factors that influence the decision between 3D printing and CNC machining. Though both technologies work well with plastics and metals, they behave differently with these materials. Let’s understand this further:
Though CNC machining has primarily been used to produce metal parts, it’s also quite flexible to manufacture parts from thermoplastics and acrylics. If you are considering CNC machining, then the material must have excellent mechanical and thermal properties. In addition, it should demonstrate a fully isotropic behavior.
Some of the most common plastics that can be used for CNC machining include ABS, Nylon, Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride, PEEK, PMMA, HDPE, LDPE, etc.
3D printing is largely used to create parts from thermoplastics and thermosets. 3D printing technology can be used to manufacture parts from a wide variety of materials that are sometimes difficult to machine such as TPU and metal superalloys.
Some of the most common materials that can be used for 3D Printing include ABS, Nylon, TPU, PP, Silicone, etc.
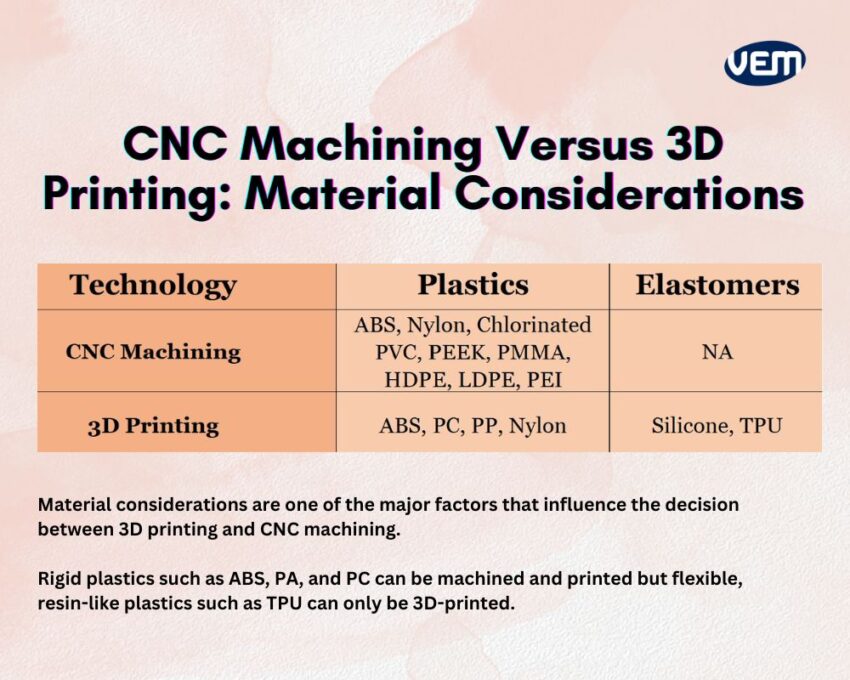
Rigid plastics such as ABS, PA, and PC can be both machined and printed via CNC machining and 3D printing respectively but flexible, resin-like plastics such as TPU can only be 3D-printed.
If the manufacturing conditions are right, then CNC machines can deliver a better-quality surface finish than 3D printers.
3D printers are usually used to design prototypes and create parts that typically need further processing whereas CNC machines are employed to manufacture final products that are usually market-ready thus, the surface finishing capability of CNC machines is much more advanced than 3D printing.
If the strength of the part is a priority, then CNC machining is an apt choice but if aesthetics are more important, as in prototypes, then 3D printing is a better choice.
CNC machined parts demonstrate better mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties as they are isotropic. 3D printed parts, on the other hand, are anisotropic as they are built layer by layer thus, they are structurally weaker.
The size of the part is not a major contributing factor because it is imperative to consider the various specifics of the project but typically, CNC machines can handle larger parts because of their sizes. 3D printers can also handle large parts but they have various costs associated that may make creating a part size beyond a certain level unfeasible.
Part complexity constitutes another major factor that must be considered when choosing between 3D printing and CNC machining technologies. Though both technologies have limitations, CNC machining has more limitations than 3D printing.
In CNC machining, there are several limitations with respect to design, tool access, and mount points. As the tools in CNC machining can’t access all surfaces of the part, some geometries are impossible to manufacture. For instance: The CNC technique is unable to machine square corners due to tool geometry. You should note that sometimes, even the 5-axis CNC machine systems aren’t always able to access some surfaces rendering some of the geometries impossible to machine via CNC. If the geometry is complex, then it will require the operator to rotate parts such that the cutting tools can access the various angles of the part geometry thus, CNC machining should be applied to part geometries that are simpler and do not require repositioning.
3D printing, on the other hand, can create complex geometries more easily. This is one of the defining and key strengths of 3D printing techniques. Since they develop directly from the CAD model, 3D printers can create the most complex geometries. 3D printing is not dependent upon inputs from operators and experts thus, it is possible to develop complex designs. In addition, it can also handle hollow designs and various other features that are usually not possible via CNC machining or other manufacturing techniques
In FDM, support structures may be required but when combined with post-processing techniques, it is possible to create extremely complex designs. In the case of SLS and MJF, which are polymer-based powder bed fusion processes, it is possible to create freeform and complex geometries without support structures.

The workflows of the manufacturing processes play a significant role in finalizing the technique. In addition, there are various post-processing methods that are applied to both 3D printing and CNC machining in order to improve the aesthetics and functionality of the part. Let’s understand the CNC machining and 3D printing workflow and post-processing methods better:
CNC machining is a comparatively, more labor-intensive process. In this process, the operator first decides various factors such as the cutting path, tool selection, spindle speed, and repositioning of the potential part, and then the block is set in the machine manually. It’s also essential to note if the part will be completely ready after machining or will need to undergo post-processing. Some of the post-processing technologies that are used for CNC machining are bead blasting, Type II & Type III anodizing, and powder coating.
In the case of 3D printing, the last steps are more labor-intensive than the initial steps. In 3D printing technology, first, the operator prepares the digital file and chooses the orientation of the block. The digital file goes to the machine, and now, the printer builds the part. When the printing is complete, the part will be cleaned and if required will go through post-processing. Some of the post-processing technologies that are used for 3D printing are media blasting, sanding and polishing, micro-polishing, and metal plating.
We have understood the various parameters that you should pay attention to and now, let’s summarize essential parameters that can help you make the right choice for your business.
You should note that if the production volume requirement is more than 500 parts, then neither 3D printing nor CNC machining is a cost-effective option. You should then consider injection molding to produce higher quantities of parts. These technologies are generally the most economical way to produce parts on a large scale!
Both CNC machining and 3D printing are very popular technologies and they both have their advantages and disadvantages in manufacturing. Choosing the right technology for a particular application is dependent upon various factors such as part complexity, material, and required precision.
At VEM-Tooling, we have a team of design experts and engineers who can help you choose the right technology for your project! Our team has vast experience and they focus on delivering high-quality products with accurate results. If you have any questions in determining which technology, you can contact us and we will get back to you right away!