

Plastic injection molding techniques offer various advantages such as outstanding toughness, light-weightiness (when compared to other materials), and easy molding at low production costs. These are just some of the reasons that plastic injection molding has gained immense popularity in the manufacturing sector.
Plastic is also an ideal substitute for glass and is thus considered for manufacturing clear, plastic parts, optical devices, and various packaging products. If clear plastics are applied for manufacturing, they are not only required to be extremely clear i.e. transparent but also to demonstrate impact and abrasion resistance.
Clear plastic injection molding requires more finesse in design and manufacturing as clear plastics don’t hide any defects, flaws, or impurities. Thus, plastic selection, tooling, and molding processes must be precise.


Injection molding of clear plastics considers not only the type of plastics but also the technology, equipment, and molds to ensure that these plastics that are substitutes for a glass exhibit an outstanding surface finish. Due to its high aesthetic requirements, clear plastic injection molding is more challenging than regular injection molding processes and thus, requires expertise and experience! In this article, we explain the injection molding of clear plastics and the factors that need to be paid attention to during the design and production processes.
The mold needs to correspond well to the plastic! Thus, it is crucial to choose the right type of clear plastic before starting mold production. You need to consider various physical and chemical factors such as mechanical strength, rigidity, UV, scratch and chemical resistance, temperature range, shrinkage rate, electrical insulation, etc. in order to choose the right transparent plastic for your project. Let’s understand further, the types of clear plastics that are available for injection molding.
There are various plastics that offer distinct advantages. Let’s discuss some of the most popular transparent thermoplastics that are available and applied to manufacture clear parts through injection molding.

Acrylics are transparent thermoplastics and demonstrate outstanding strength and stiffness. Acrylic is a lightweight, shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It is seventeen times more impact resistant than glass and is easier to handle and process. They not only exhibit glass-like qualities in terms of transparency and clarity but they do so at half the weight of glass!
Acrylic sheets, also known as plexiglass or acrylic glass are easy to fabricate and they bond well with adhesives and solvents. Since acrylics demonstrate UV-resistant, impact-resistant, non-toxic, and scratch-proof properties, at half the weight of glass, they are preferred by a variety of industries. It’s applied in skylights, displays, shelves, and outdoor equipment. Its ability to evenly distribute additives such as colorants throughout the part is why it’s a popular clear plastic for manufacturing light fixtures, retail displays, clear swimming pools, reflectors, and colored lenses.
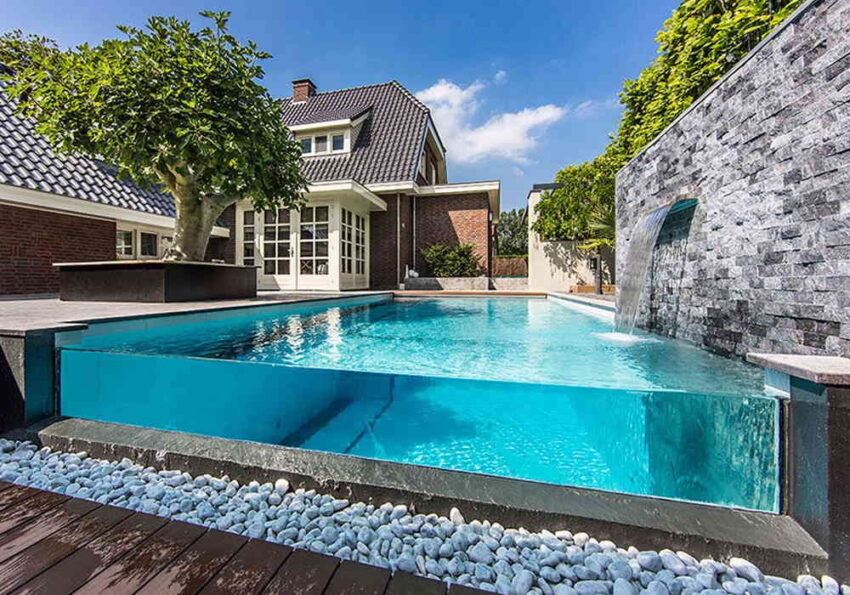

For e.g. Acrylic sheets are used to manufacture clear swimming pools.
Though acrylics exhibit outstanding durability and high-aesthetic qualities, they can be brittle and inflexible. Thus, it’s not an ideal choice for plastic parts that need to undergo high pressure.
Polycarbonate is an excellent engineering plastic that is as clear as glass and is estimated to be 250 times stronger than glass. It is also 30 times stronger than acrylic but you should note, that it is also an expensive plastic! It is highly impact-resistant and shares the same transparency and UV resistance as acrylic. They are particularly useful when impact resistance and transparency are prerequisites for an application. It is commonly used to manufacture medical devices, automotive components, protective gear, and exterior lighting fixtures.
Polycarbonates exhibit very good heat resistance and they can be combined with flame-retardant materials without causing significant material degradation. They are designed to be stronger and comparatively resistant to extreme temperatures. Thus, polycarbonates are particularly used to design plastic parts that are subjected to stress and extreme outdoor environments such as safety goggles, helmets, shields, heavy-duty containers, and safety windows.
The most commonly used clear plastics are Acrylics and Polycarbonates. They meet most of the application requirements. We have listed some of the major differences below:
Polyetherimide, abbreviated for PEI is an amorphous thermoplastic resin with amber transparency. This transparent material is often seen in automotive, electrical, and medical industries due to its ability to tolerate extreme temperatures and continual forces.
PEI is characterized by its high deflection temperature (200°C / 392°F at 264 psi / 1.82 mPa), high tensile strength, and very good retention of mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. PEI is UV resistant and can withstand intense pressure and heat. PEI is inherently flame resistant without the use of additives and maintains its chemical stability when in contact with acids. It is thus applied in heat shields, temperature sensors, aerospace engine components, and various electrical parts and covers.
Polypropylene, abbreviated for PP, is a naturally transparent amorphous thermoplastic and highly flexible.
It is commonly used in textiles, packaging, and containers. Since it demonstrates high electrical resistance, it is widely applied in electronics. In addition, PP does not react with acids and bases. It thus makes a good container for solvents and other corrosive materials.
Plastic transparency is directly proportional to light transmittance i.e. higher the transmittance percentage, the higher would be the transparency.
The transmission of visible light (plastic transparency) is characterized by light transmittance, i.e. the measured percentage of incident light transmitted through the plastic. Transparency has no specific unit. It is reported in the percentage of light transmitted.

Plastic transparency depends on the type and structure of the polymer, its crystallinity, and the types of additives used. Generally, amorphous plastics such as acrylics, PC, and PEI are transparent whereas semi-crystalline or crystalline polymers such as PE, PET, and Nylon are translucent or opaque. Plastic transparency can be measured through 2 main parameters:
Light transmittance is defined as the light percentage that passes through the transparent material. You should note that no material has a light transmittance of 100%. In general, light transmittance is about 92% for Acrylics, 90% for Polycarbonates, and 95% for optical glass.
Haze is the light scattering when it passes through an object. A transparent material is more clear when it has a high light transmittance and a low haze measurement. A transparent plastic that is characterized by good clarity has a haze measurement of less than 2%.
Light-diffusing materials are characterized by having a high light transmittance and a high haze value. They are often used in covers for LED lights and LED indicators so that the light is even and dazzles less.
Clear plastic parts have higher aesthetic requirements. They need to be devoid of any defects as they are easily see-through. You must note that a clear plastic part project is more challenging than regular injection molding projects as blemishes and defects are easily visible in transparent parts. Let’s understand some of the most common defects that may occur and how product teams can avoid them.

Flow lines are off-color lines or streaks that appear on the surface of a part. These are caused by the molten plastic shots moving at different speeds in the mold, which ultimately causes the resin to solidify at different rates. This is often a sign that either the injection speed or the pressure or both, are too low.
Sink marks appear as depressions, dents, or craters in thick sections of a plastic part. Thicker sections take longer to cool, which can cause the inner portions of the part to contract at a much different rate than the outer sections. The main impact of sink marks is aesthetical. Sinks marks are often a consequence of poor design that may be caused due to uneven wall thickness.
Delamination is a condition that causes a part’s surface to separate into thin layers. These layers appear as coatings and they can be easily peeled off. They are caused due to the presence of contaminants in the material. You should note that excessive use of mold-release agents can also cause delamination.
Surface delamination can be prevented by increasing mold temperatures and optimizing the mold ejection mechanism to be less dependent on mold-release agents since these agents increase the risk of delamination.
A weld line mark occurs when two flows of molten plastic meet as they flow through the mold. This usually happens around the geometry part that has a hole. As the molten plastic flows around the hole and the two flows of the plastic meet, there is a potential for weld line formation.
If the temperature of the flow isn’t just right, the two flows won’t properly bond together and will instead cause a visible weld line. This not only causes a visual defect but also reduces the overall strength and durability of the component.
Plastic warping refers to unintended twists or bends in the plastic part. Warping defects are caused due to inconsistent mold cooling. Plastic warpage can be prevented by ensuring that the plastic parts are given enough time to cool to prevent internal stresses from forming.
Silver lines, also known as splays, are clusters of silver streaks that are formed on the surface of the plastic part. These lines are usually arranged in the way of flow direction. Silver streaks affect the appearance or the material performance.
Clear plastic parts have exceptionally high aesthetic and optical clarity requirements. Thus, there are stringent requirements for the machining and polishing of the molds.
It is crucial to hold the machining within a tight tolerance. This ensures that the polishing is minimal which reduces any possibility of distortion or waviness on the reflected image thus, it does not change the geometrical properties. Otherwise, the same distortion or waviness can appear on the molded parts as well.
Many clear plastics are stiff-flowing materials. They have low flowability which can cause excessive internal stress. This can lead to injection molding defects such as cracking, flow lines, silver lines, and vacuum voids. It is thus advised to locate the gate at the thick-wall area, and make the gate larger if possible. This helps to fill the cavity quickly and easily thus, enabling enough packing pressure to compensate for the shrinkage in the packing stage.
Proper part design is critical to eliminate possible injection defects. It is thus advised to have an appropriate wall thickness and keep it even all over the part. In the case of PC and Acrylics, the recommended wall thickness should be greater than 1mm. In addition, a slightly larger draft angle can avoid scratches on the vertical side. Thus, a proper part design can help eliminate surface defects.
It is always recommended to conduct a thorough mold flow analysis. This practice enables the manufacturer to check the pressure, temperature, and tendency of forming weld lines and air bubbles. It also helps the manufacturer to fine-tune the gate and part design.
Air traps in the mold can lead to various types of defects such as air bubbles, short shots, flashes, and burning. It is imperative to include adequate mold venting according to the plastic viscosity. This prevents air traps in the mold. This is one of the reasons why changing plastic material after a mold is made can be a problem.
If the screws and barrels of the injection molding machine are not completely cleaned, they can randomly introduce impurities in some of the molded plastic parts. Thus, it’s imperative to clean the barrels and screws thoroughly.
Clear plastic parts have a high light transmittance and thus, the surface quality should be impeccable. There must be no scope for defects such as any type of markings, whitening, black spots, discoloration, poor gloss, etc. Thus, great attention needs to be paid to the entire injection molding process.
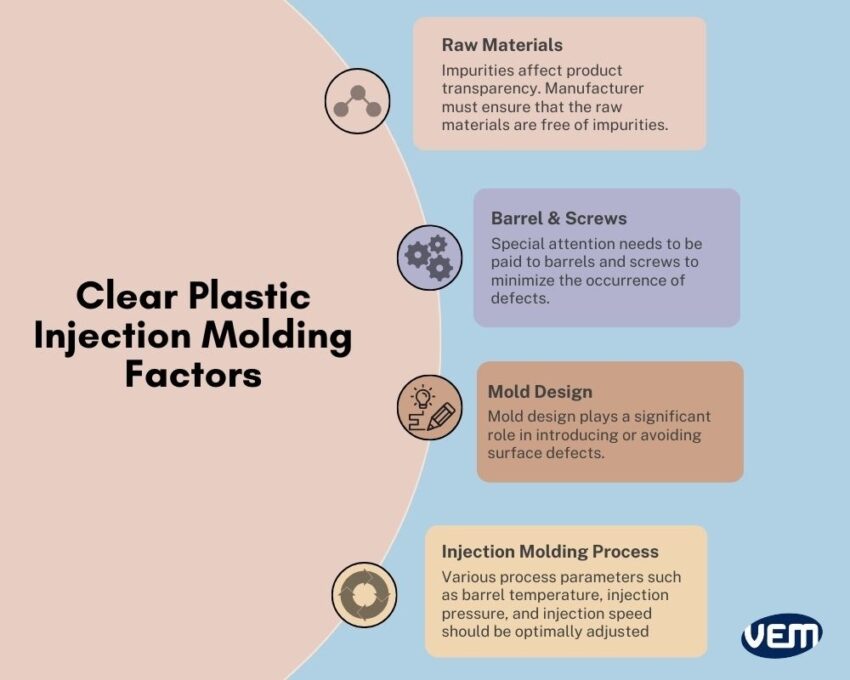
Plastic impurities affect product transparency thus, the manufacturer must ensure that the raw materials are free of any impurities. This should be maintained throughout the process of storage, transportation, and feeding.
You should also note that certain plastic resins such as Acrylics tend to absorb moisture, which causes deterioration of the raw material after heating, so it must be dried thoroughly. The manufacturer should ensure that the input air should be filtered and dehumidified to ensure that the raw materials are not contaminated.
Impurities in the recesses of screws and accessories can introduce contamination thus, the screws should be cleaned thoroughly before use and after the shutdown to avoid impurities. If a screw cleaning agent isn’t available, the screw can be cleaned with either polyethylene or polystyrene resin.
During a temporary shut-off, the temperature of the dryer and the barrel should be lowered to prevent the degradation of raw materials due to high-temperature exposure.
Mold design plays a significant role in introducing or avoiding surface defects. In order to ensure a high-quality surface finish that is devoid of defects, the manufacturer should pay attention to the following factors:
You should also note that clear plastics generally have a high melting point and poor fluidity. Thus, various process parameters such as barrel temperature, injection pressure, and injection speed should be optimally adjusted. It should be ensured that the mold fills without any internal stresses to ensure that the surface quality of the plastic parts is maintained and they are without any deformation. In order to reduce internal stress, the following factors should be ensured:
Injection molding clear plastic parts require stricter processing controls and focused attention compared to non-transparent injection molding. Clear polymers have varying properties such as differing levels of strength, temperature requirements, and chemical resistance. It is thus imperative to determine which of these plastics is best suited for your project.
At VEM Tooling, we can help you determine the right type of clear plastic for your part and can assist with prototype development to ensure integrity. If you have questions about transparent plastic resins or injection molding in general, contact us today.