

Plastic parts such as cardiac products or any medical device need to be as clean and sterile as possible. There can be no question of dirt particles or fibers while manufacturing such parts which is why they are always manufactured in a sterile environment. This type of sterile environment is referred to as a ‘cleanroom.’ In this article, we explain in detail about injection molding and production in general, in a cleanroom.
Certain industries such as medical, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries require that the plastic parts are manufactured in a sterile environment so that there is no risk of contamination. To eliminate the risk of contamination from dust or other particles, a dedicated room is optimized.
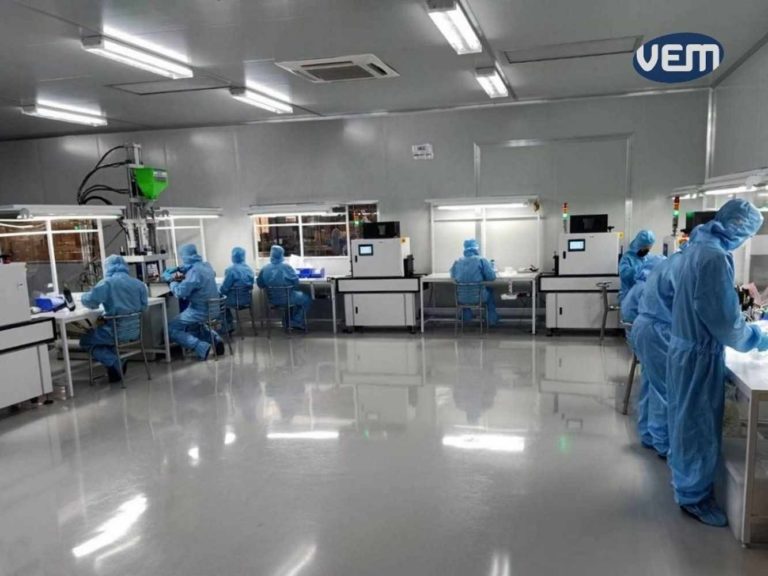

A cleanroom in the injection molding industry is a controlled environment to eliminate contamination. In the clean room, the number of airborne contaminants per unit volume is controlled by HEPA, abbreviated for High-Efficiency Particulate Air.
A cleanroom in the injection molding industry is a controlled environment to eliminate contamination. In the clean room, the number of airborne contaminants per unit volume is controlled by HEPA, abbreviated for High-Efficiency Particulate Air.
HEPA filters clean the air before entering the cleanroom to remove contaminants such as dust and microbes. This is done several times per hour, according to the cleanroom class. These standards are established by the International Standard Organization (ISO) 14644-1.
Clean rooms in general, must control various types of environmental conditions. These range from temperature, humidity, and pressure to ventilation. There are various features to creating and maintaining a cleanroom. This is optimized by following 4 major protocols:

There are various types of clean rooms and each clean room environment has different requirements. These different requirements can feature either solid wall elements i.e. a hardwall or foil curtains i.e. a softwall.
A softwall cleanroom is a confined space with a metal frame. It has clear panel walls with an entrance, high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters, and exceptional lighting. It is designed to provide a contaminant and particulate matter-free workspace.
In the case of softwall cabins, PVC curtains shield the local clean air area against environmental influences. There are several fan-filter modules that ensure the supply of pure air. The exhaust air can easily escape the clean room from, under the curtains.
Softwall cleanrooms can vary from 4 feet by 4 feet up to 24 feet by 36 feet. These standard sizes make them extremely flexible to design and thus, one can create softwall designs of multiple configurations and sizes.
The most important criteria for softwall cleanrooms are to meet the requirements for their ISO classification. The design of softwall cleanrooms, however, does not make it possible for them to meet the highest ISO standards. This is because they are not capable of being tightly sealed as rigid and hardwall cleanrooms.
In the case of hardwall cabins, it is possible to quickly create a clean environment for a specific process. Hardwall cabins can be adapted to suit your requirements. In addition, there are standardized segments that enable a simple setup of different cabin sizes.
A hardwall cabin system can be constructed with aluminum and its wall elements can be made of glass, PVC, or PMMA. Each material has its advantages and disadvantages – These should be considered beforehand and prior to the construction of a cleanroom.
Clean room molding requirements differ in various segments from a typical injection molding floor. This section indicates the basic requirements of a clean room for injection molding.
Any components, other than raw material, that have to enter the cleanroom, need to go through a negative pressurization chamber. In there, any dust particles will be removed before granting passage into the cleanroom.
Finished goods that have been produced and sealed in the cleanroom are also being transported through this loading system.
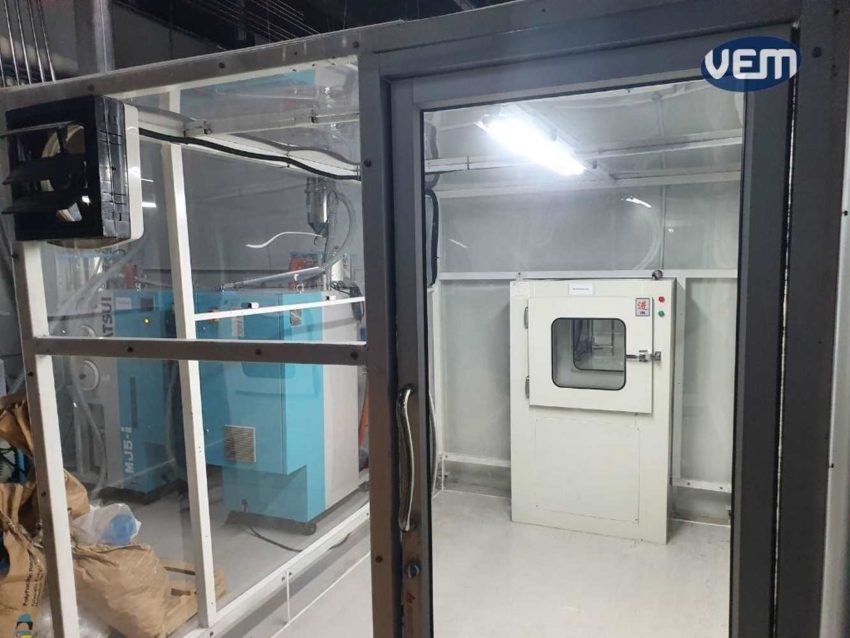

Material Drying Equipment is kept outside the clean room. It requires little or no maintenance from within the cleanroom and is sealed keeping any contaminants from entering the cleanroom environment.
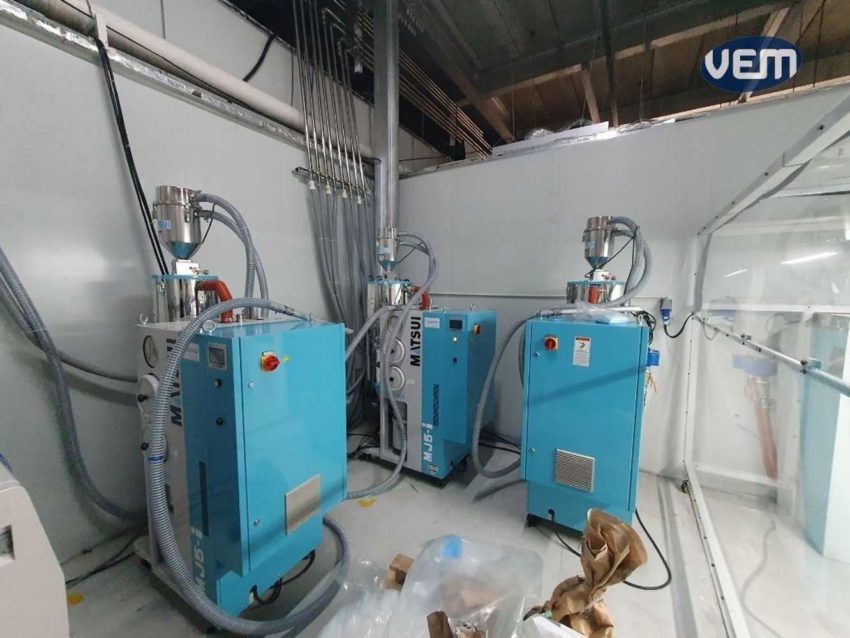

Keeping the material drying equipment outside is imperative as loading the dryers, and trying and taking the material out poses several risks of contamination of the cleanroom. Therefore, the whole system is located outside in a safe environment.
The drying equipment is connected to the feeding equipment. In addition, a maintenance check is carried out every year so that there is virtually no risk of contamination to the cleanroom environment.
Injection molding machines need to be cooled through water when they are under production. In the case of a cleanroom, the chiller device that brings the water to a preferred temperature is located outside of the cleanroom. The chiller device pulls the air from outside and gets warm which is why in a cleanroom environment, it is preferred to be outside. Thus only the pipes with cold or warm water are designed to go in.
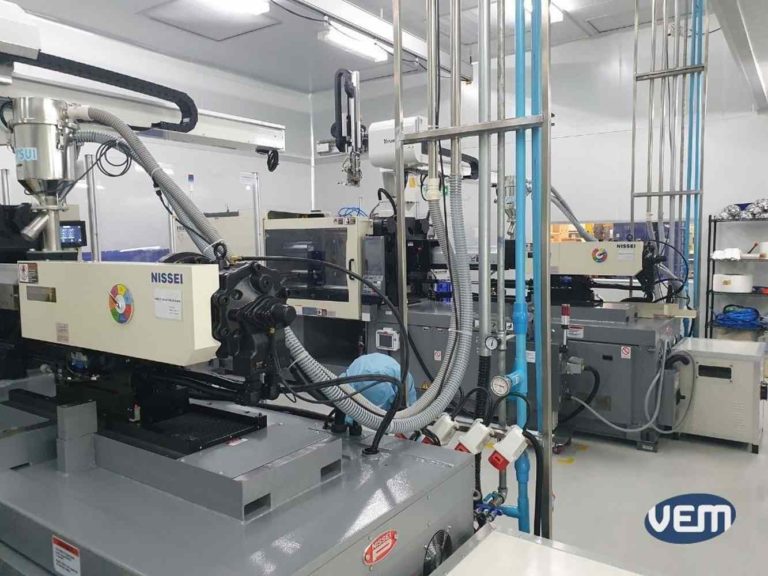

The cold water goes into the cleanroom, and cools the machine or mold, after which the warm water goes out of the cleanroom which will be chilled. The pipes enable the chilling without causing a risk of contamination.
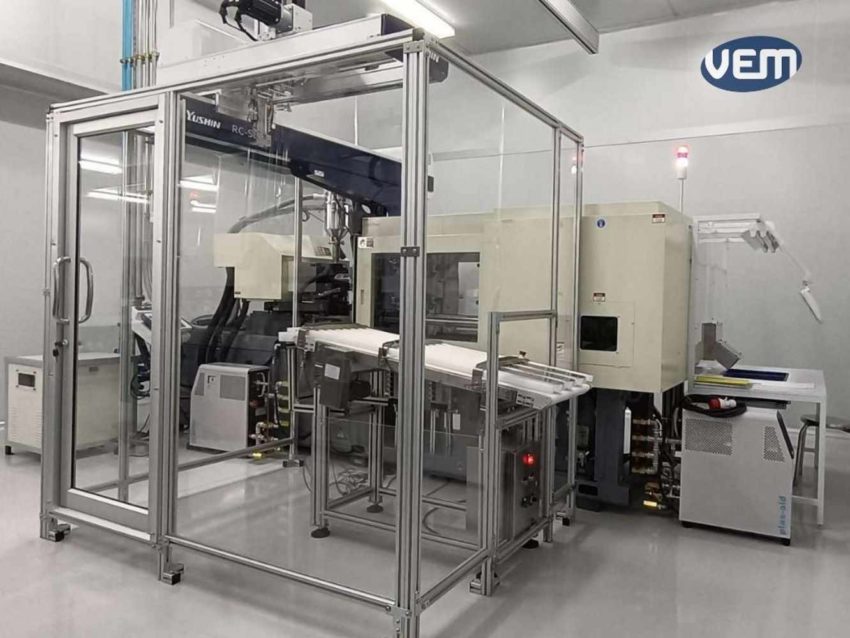
Generally, an injection machine can be hand fed, especially for very small production runs or sampling procedures. In most high volume production, a feeder is hooked onto the machine which sucks the plastic material into the machine. The feeder is most of the time in close range to the material dryers.
Since a cleanroom does not allow dryers to be inside, there have to be pipes that transport the plastic resin to the machines. As it can be seen on above picture, the pipes are coming from the ceiling and will directly move the material into the machine.
This allows a clean and contamination free loading process of the injection machine.
Electric machines generally replace hydraulic machines in clean rooms to avoid the occurrence of particulates in the air. This is because hydraulic machines don’t have as many motors, joints, gear mechanisms, and subsystems. Electric machines on the other hand eliminate the hoses, filters, tubes, and valves of a hydraulic system. Thus, electric machines reduce the risk of contamination.

Positive Pressure means that the air pressure inside the clean room is greater than the pressure outside of it. Positive pressure air flow is created when clean, filtered air is pumped through the ceiling into the cleanroom.
Positive pressure is generally used if keeping contaminants out of the cleanroom is a priority. If there is a leak, clean air will be forced out of the cleanroom instead of unfiltered air entering the cleanroom.
In a negative pressure cleanroom, the air pressure in the room is lower than the pressure outside of the room which is created by filtering air out of the room. All the outlets i.e. the windows and the doors are completely sealed. Thus, it creates a lower pressure within the room which results in outside air flowing into the cleanroom.
Negative pressure is used when the priority is to keep any possible contamination escaping from the cleanroom.
Air filtration systems are employed to limit the contaminants in the air. There are 2 types of filters that are primarily employed: HEPA filters and ULPA filters. They both use a combination of diffusion, interception, and inertial impaction to remove contaminants. These filters remove approximately 99.9% of microparticles from the environment however there are major differences in the particulate matter size.
It is also important to understand the MERV rating which describes a filter’s capability to capture contaminants. MERV, abbreviated for minimum efficiency reporting values rates filters between 1 to 16. The below diagram indicates the various MERV ratings for the average particle size efficiency in Microns.
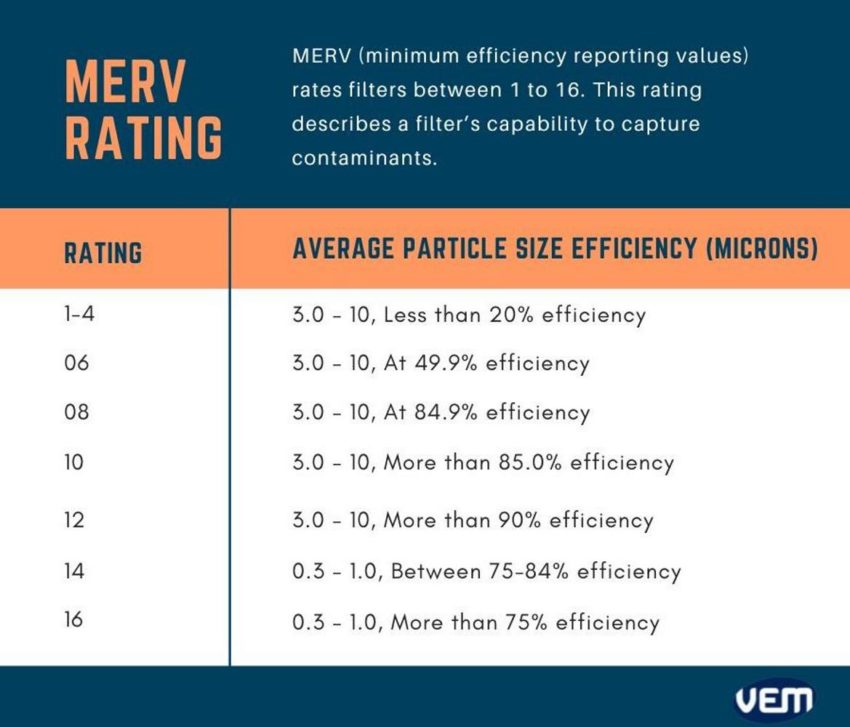
HEPA, abbreviated for high-efficiency particulate air, is a type of mechanical air filter that can remove at least 99.9% of the contaminants from the air with 99.97% efficiency. It can remove all types of dust, pollen, airborne particles, and bacteria that have a diameter specification of up to 0.3 microns. This size of 0.3 microns is regarded as the most penetrating particle size (MPPS).
ULPA, abbreviated for ultra-low particulate air, is a high-efficiency filter that’s 99.99% effective at removing submicron particles. It can remove particles of 0.12 microns and larger.
ULPA filters are usually less effective in reducing the overall particle concentration and they also require more power to move air.
Cleanroom airflow can be categorized as unidirectional (laminar), non unidirectional (turbulent), or mixed (combination of unidirectional and non unidirectional zones) flow.
In the Laminar air flow system, the air flows in a straight, unimpeded path. It generally utilizes HEPA filters to filter air entering the environment. If the cleanroom includes a laminar system, it is referred to as a unidirectional airflow cleanroom.
Non-unidirectional airflow generally uses turbulent airflow systems to maintain a clean environment. Turbulent airflow can cause particle movement that can be difficult to separate from the rest of the air, but non-unidirectional airflow systems count on random movement to move particles from the air through the filter.
Cleanrooms call for the highest standards of sanitation which is why there are certain items that are not allowed in the clean room. Let’s take a look at some of the protocols followed in the clean room regarding the permitted and non-permitted items:


With regards to cleaning material, only approved materials must be used. Mops, disinfectants, cleanroom wipes, and vacuum cleaners are permitted as long as they meet industry cleanroom standards.
There are various apparel requirements that one needs to adhere to while entering a clean room. Cleanroom garments such as coveralls offer superior particulate and light barrier protection. We have listed some of these protocols below:
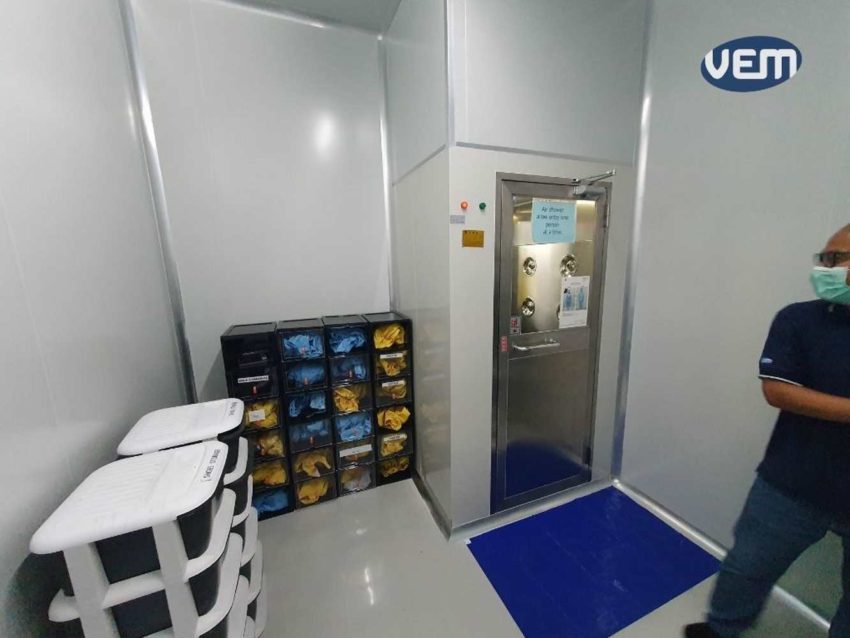
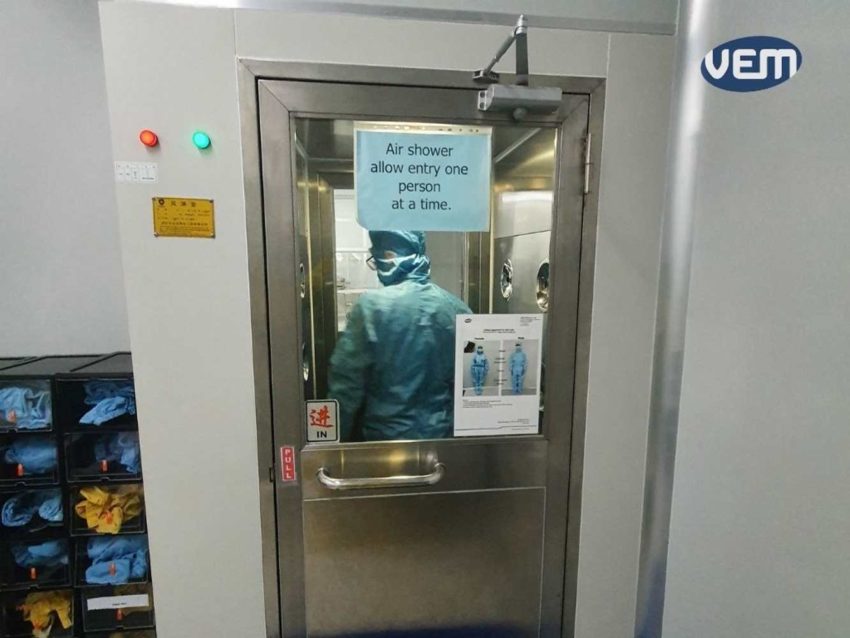


Vacuums that can be safely operated around electrical equipment and include HEPA and other filters should be used. There are some vacuums that also offer a multi-stage filtration system. This helps to capture more than 99% of the dust.
Adhesive rolls and mops with low contamination characteristics are also suitable for keeping cleanroom walls and floors clean provided they are permitted according to the standards.
There are certain packaging materials that are not allowed in clean rooms. These are certain corrugated materials that may produce additional particulates such as coated cardboard or plastic packaging.
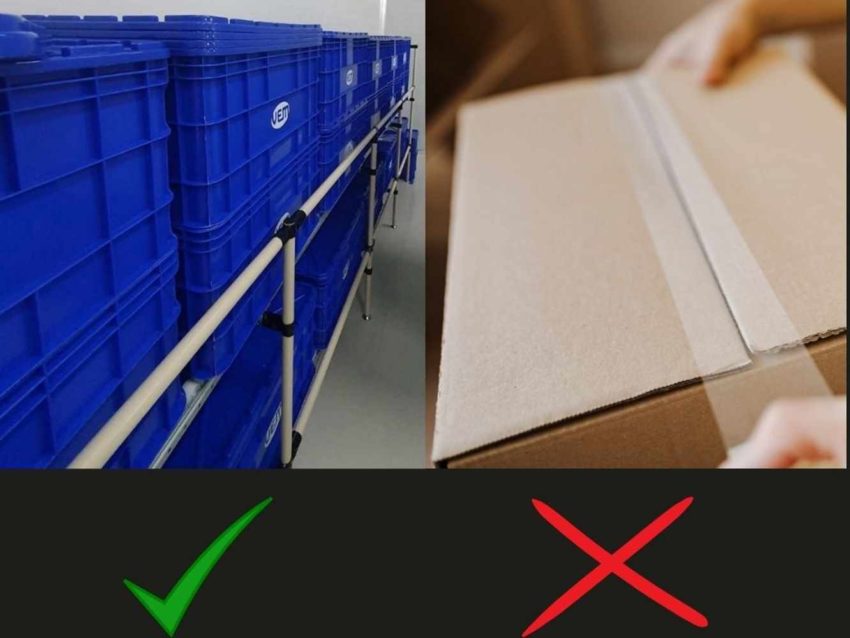

A cleanroom is classified according to the number and size of particles permitted per volume of air. There are 3 standards that have been developed to classify cleanrooms:
Both the classification standards FS 209E and ISO 14644-1 measure specific particle count to classify the cleanliness level of a cleanroom.
Clean rooms need to be qualified for manufacturing medical devices and thus, need to acquire certain certifications such as GMP, FDA, and ISO 13845:2016.
GMP: GMP, abbreviated for Goods Manufacturing Practice is a system that is responsible for ensuring that the entire manufacturing process is consistent and in line with the quality standards. GMP reduces production-related risk by covering each and every aspect of the production process.
ISO 13845: Just like the GMP, ISO 13485 is another system that is designed to ensure the production of medical devices in clean room. ISO standards undergo revision every 5 years in order to keep up with the marketplace trend. Today, ISO 13485:2016 is the latest standard that responds to the current quality control practices.
FDA: FDA abbreviated for, Food and Drug Administration (FDA) instates that the manufacturer needs to establish and maintain procedures to adequately control environmental conditions. According to FDA, it is imperative that the cleanroom is in a controlled environment.
Process documentation is one of the most important aspects of maintaining quality for clean room injection molding.
It is imperative that the cleanroom injection molders adhere to various variables in order to ensure that they comply with the standards. Such variables include all types of quality control systems that check, control and eliminate any type of dust and particles that do not comply with the specification of the cleanroom standards. Thus, it is essential that the procedure documentation is carried out to ensure that the verification of controlled conditions is always available in events of customer request, routine check, procedural deviation, or repeated cycles.
ISO stands for International Standard Organization which comprises various organizations from different countries. These countries work together to develop and publish standards that are internationally valid and thus, need to be adhered to across borders.
Since 2001, the cleanroom classification of classes ISO 1 – ISO 9 of ISO 14644-1 has been in effect. ISO 14644-1 defines the degree of purity of the air by determining limit values. ISO classification is upon the basis of particle concentration per m³. The highest purity in ISO 14644-1 is in ISO class 1, whereas the lowest is classified as ISO class 9. ISO Class 9 is also categorized as Room air. The table below depicts the ISO 14644-1 Cleanroom Standards:
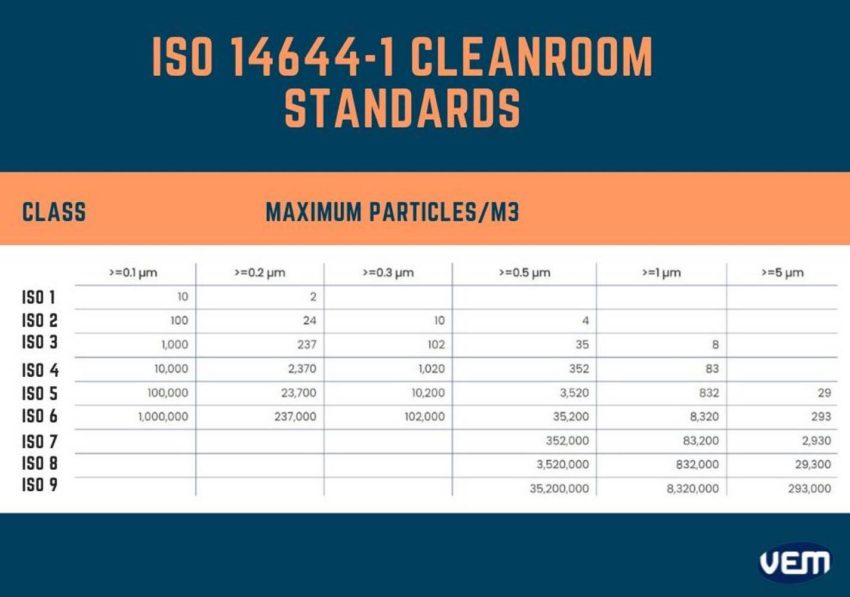
Generally, most plastic cleanroom injection molding requirements are either a Class 7 or Class 8 cleanroom. It may however require a more sterile environment, if the plastic part has a very low resistance to impurities, such as used lenses in thermal imaging telescopes.
ISO 7 cleanroom is a closed area. Hard walls are used to separate it from the rest of the business area. ISO 7 is mostly used for surgical interventions without implantation of foreign materials such as low invasive surgery, vascular, obstetrics, and ophthalmology.
ISO 8 classrooms have less stringent standards than those for ISO 7 cleanrooms. In the ISO 7 cleanroom, the store’s molds are surrounded by movable curtains. ISO 8 is used for short-term surgery such as urology and day surgery.
Cleanroom injection molding can be applied to a variety of industries. We have listed some of the applications below:

Injection molding factories generally have Class 8 level cleanrooms however, If you are manufacturing implantable medical devices, then you will need to manufacture in Class 8 Cleanroom. Thus, cleanroom class requirements need to be aligned with your project requirements.
To ensure that your plastic part is as clean as possible, you must search for a manufacturing partner that cannot only mold but also assemble, and package your product in the cleanroom. This ensures that the plastic part is as clean as possible.
An injection molding company can have various cleanroom capabilities but if your project requires molding complex plastic parts and difficult part tolerances, then you need to ensure that the injection molding company is equipped to hold tight tolerances. This expertise is necessary to ensure that every plastic part is not just clean but is also high in quality.
VEM Tooling has several clean rooms in our facility in Thailand. Not only does our team have the expertise for clean room injection molding, but we also offer dependable service with quick quotes. Contact us and a team member will connect with you to resolve your queries.